Prevention of vasa vasorum neovascularization attenuates early neointima formation in experimental hypercholesterolemia
- PMID: 19458984
- PMCID: PMC2978040
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-009-0036-0
Prevention of vasa vasorum neovascularization attenuates early neointima formation in experimental hypercholesterolemia
Abstract
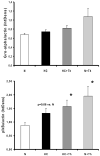
Vasa vasorum (VV) neovascularization is a key feature of early atherosclerosis and adds substantial endothelial exchange-surface to the coronary vessel wall. Thus, it is conceivable that VV neovascularization favors the entry of pro-inflammatory and pro-atherosclerotic blood components into the coronary vessel wall. We sought to investigate the effects of Thalidomide (Th), a potent anti-angiogenic drug on vasa vasorum (VV) neovascularization, vessel wall inflammation, and neointima formation in early experimental atherosclerosis. Female domestic swine, 3 months old, were fed normal (N, n = 12) or high-cholesterol diet (HC, n = 12) for 3 months. In each group six pigs were randomized to 200 mg Thalidomide daily for the diet period (N + Th, HC + Th). LADs were scanned with micro-CT (20 microm cubic voxel size) to determine VV spatial density (#/mm2). Fresh-frozen coronary tissue was used for western blotting (VEGF, TNF-alpha, LOX-1, Ikappabetaalpha and Gro-alpha) and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA, NFkappabeta). Treatment with Thalidomide preserved VV spatial density [2.7 +/- 0.3 (N), 6.4 +/- 0.7 (HC), 3.5 +/- 0.8 (HC + Th); p = ns HC + Th vs. N] and inhibited the expression of VEGF, TNF-alpha and LOX-1, but not NFkappabeta activity in the coronary vessel wall. Immunofluorescence analyses revealed co-localization of vWF but not SMA and NFkappabeta, TNF-alpha as well as VEGF in HC and HC + Th coronaries. Intima-media thickness was significantly inhibited in HC + Th compared to HC. Serum levels of hs-CRP and TNF-alpha did not differ among the groups. Our study supports a role of VV neovascularization in the development of and a therapeutic potential for anti-angiogenic intervention in early atherosclerosis.
Figures






References
-
- Aydogan S, Celiker U, Turkcuoglu P, Ilhan N, Akpolat N. The effect of thalidomide on vascular endothelial growth factor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008;246:363–368. - PubMed
-
- Caunt M, Hu L, Tang T, Brooks PC, Ibrahim S, Karpatkin S. Growth-regulated oncogene is pivotal in thrombin-induced angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2006;66:4125–4132. - PubMed
-
- Chade AR, Best PJ, Rodriguez-Porcel M, Herrmann J, Zhu X, Sawamura T, Napoli C, Lerman A, Lerman LO. Endothelin-1 receptor blockade prevents renal injury in experimental hypercholesterolemia. Kidney Int. 2003;64:962–969. - PubMed
-
- Chew M, Zhou J, Daugherty A, Eriksson T, Ellermann-Eriksen S, Hansen PR, Falk E. Thalidomide inhibits early atherogenesis in apoE-deficient mice. APMIS. 2003;(Suppl):113–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

