Enhancement of oral bioavailability of cilostazol by forming its inclusion complexes
- PMID: 19459053
- PMCID: PMC2690812
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-009-9249-7
Enhancement of oral bioavailability of cilostazol by forming its inclusion complexes
Abstract
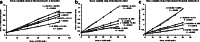
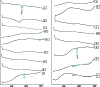
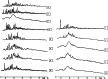
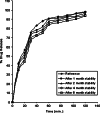
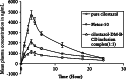
The study was designed to investigate the effect of cyclodextrins (CDs) on the solubility, dissolution rate, and bioavailability of cilostazol by forming inclusion complexes. Natural CDs like beta-CD, gamma-CD, and the hydrophilic beta-CD derivatives, DM-beta-CD and HP-beta-CD, were used to prepare inclusion complexes with cilostazol. Phase solubility study was carried out and the stability constants were calculated assuming a 1:1 stoichiometry. Solid cilostazol complexes were prepared by coprecipitation and kneading methods and compared with physical mixtures of cilostazol and cyclodextrins. Prepared inclusion complexes were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies. In vitro dissolution study was performed using phosphate buffer pH 6.4, distilled water, and HCl buffer pH 1.2 as dissolution medium. The optimized inclusion complex was studied for its bioavailability in rabbit and the results were compared with those of pure cilostazol and Pletoz-50. Phase solubility study showed dramatic improvement in the solubility of drug by formation of complexes, which was further increased by pH adjustment. The dissolution rate of cilostazol was markedly augmented by the complexation with DM-beta-CD. DSC and XRD curves showed sharp endothermic peaks indicating the reduction in the microcrystallinity of cilostazol. Selected inclusion complex was also stable at ambient temperature up to 6 months. The in vivo study revealed that DM-beta-CD increased the bioavailability of cilostazol with low variability in the absorption. Among all cilostazol-cyclodextrins complexes, cilostazol-DM-beta-CD inclusion complex (1:3) prepared by coprecipitation method showed 1.53-fold and 4.11-fold increase in absorption along with 2.1-fold and 2.97-fold increase in dissolution rate in comparison with Pletoz-50 and pure cilostazol, respectively.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inclusion complexes of tadalafil with natural and chemically modified beta-cyclodextrins. I: preparation and in-vitro evaluation.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008 Nov;70(3):819-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.06.024. Epub 2008 Jul 4. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008. PMID: 18655829
-
Effects of the Preparation Method on the Formation of True Nimodipine SBE-β-CD/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complexes and Their Dissolution Rates Enhancement.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015 Jun;16(3):704-15. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0257-x. Epub 2014 Dec 17. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015. PMID: 25511809 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo studies on the complexes of vinpocetine with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin.Arch Pharm Res. 2007 Aug;30(8):991-1001. doi: 10.1007/BF02993968. Arch Pharm Res. 2007. PMID: 17879753
-
Melatonin/Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes: A Review.Molecules. 2022 Jan 10;27(2):445. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020445. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35056757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short Review on the Biological Activity of Cyclodextrin-Drug Inclusion Complexes Applicable in Veterinary Therapy.Molecules. 2023 Jul 21;28(14):5565. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145565. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization, ex vivo permeation, and stability study of lipid nanocarrier loaded gelatin capsules for treatment of intermittent claudication.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Jul 13;10:4459-78. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S83123. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26203244 Free PMC article.
-
Improved oral absorption of cilostazol via sulfonate salt formation with mesylate and besylate.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jul 30;9:3961-8. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S87687. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26251575 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Surfactant Micellization for Enhanced Dissolution of Poorly Water-Soluble Cilostazol Using Poloxamer 407-Based Solid Dispersion via the Anti-Solvent Method.Pharmaceutics. 2021 May 5;13(5):662. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050662. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34063136 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic approach to design and prepare solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drug.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014 Jun;15(3):641-57. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0093-z. Epub 2014 Feb 22. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014. PMID: 24563175 Free PMC article.
-
Cilostazol-Loaded Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Electrospun Drug Delivery System for Cardiovascular Applications.Pharm Res. 2018 Jan 16;35(2):32. doi: 10.1007/s11095-017-2314-0. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 29368067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Physicians. Medical Economics . Physicians’ desk reference. 59. Stamford: Thomson; 2005. pp. 2564–6.
-
- Larsen KL. Large cyclodextrins. J Inclusion Phenom Macro Chem. 2002;43(1–2):1–13. doi: 10.1023/A:1020494503684. - DOI
-
- Szejtli J, Osa T. Comprehensive supramolecular chemistry: cyclodextrins. Oxford: Pergamon; 1996.
-
- Mosher G, Thompson D. Complexation and cyclodextrins. encyclopedia of pharmaceutical technology, Vol. 19. New York: Marcel and Dekker; 1999. pp. 49–88.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

