Lipoprotein accumulation in macrophages via toll-like receptor-4-dependent fluid phase uptake
- PMID: 19461045
- PMCID: PMC2741301
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.192880
Lipoprotein accumulation in macrophages via toll-like receptor-4-dependent fluid phase uptake
Abstract
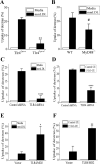
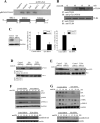
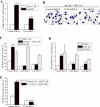
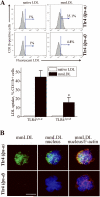
Toll-like receptor (TLR)4 recognizes microbial pathogens, such as lipopolysaccharide, and mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine secretion, as well as microbial uptake by macrophages. In addition to exogenous pathogens, TLR4 recognizes modified self, such as minimally oxidized low-density lipoprotein (mmLDL). Here we report that mmLDL and its active components, cholesteryl ester hydroperoxides, induce TLR4-dependent fluid phase uptake typical of macropinocytosis. We show that mmLDL induced recruitment of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) to a TLR4 signaling complex, TLR4 phosphorylation, activation of a Vav1-Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK1/2 signaling cascade, phosphorylation of paxillin, and activation of Rac, Cdc42, and Rho. These mmLDL-induced and TLR4- and Syk-dependent signaling events and cytoskeletal rearrangements lead to enhanced uptake of small molecules, dextran, and, most importantly, both native and oxidized LDL, resulting in intracellular lipid accumulation. An intravenous injection of fluorescently labeled mmLDL in wild-type mice resulted in its rapid accumulation in circulating monocytes, which was significantly attenuated in TLR4-deficient mice. These data describe a novel mechanism leading to enhanced lipoprotein uptake in macrophages that would contribute to foam cell formation and atherosclerosis. These data also suggest that cholesteryl ester hydroperoxides are an endogenous ligand for TLR4. Because TLR4 is highly expressed on the surface of circulating monocytes in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions, and cholesteryl ester hydroperoxides are present in plasma, lipid uptake by monocytes in circulation may contribute to the pathological roles of monocytes in chronic inflammatory diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The SYK side of TLR4: signalling mechanisms in response to LPS and minimally oxidized LDL.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov;167(5):990-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02097.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22776094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyoxygenated cholesterol ester hydroperoxide activates TLR4 and SYK dependent signaling in macrophages.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 23;8(12):e83145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083145. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376657 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor-4 and lipoprotein accumulation in macrophages.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2009 Oct;19(7):227-32. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2010.02.001. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2009. PMID: 20382346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages generate reactive oxygen species in response to minimally oxidized low-density lipoprotein: toll-like receptor 4- and spleen tyrosine kinase-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase 2.Circ Res. 2009 Jan 30;104(2):210-8, 21p following 218. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.181040. Epub 2008 Dec 18. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19096031 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 4-dependent and -independent cytokine secretion induced by minimally oxidized low-density lipoprotein in macrophages.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 Jun;25(6):1213-9. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000159891.73193.31. Epub 2005 Feb 17. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005. PMID: 15718493
Cited by
-
Dynamic T cell-APC interactions sustain chronic inflammation in atherosclerosis.J Clin Invest. 2012 Sep;122(9):3114-26. doi: 10.1172/JCI61758. Epub 2012 Aug 13. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22886300 Free PMC article.
-
The SYK side of TLR4: signalling mechanisms in response to LPS and minimally oxidized LDL.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov;167(5):990-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02097.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22776094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging applications for zebrafish as a model organism to study oxidative mechanisms and their roles in inflammation and vascular accumulation of oxidized lipids.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Oct 1;53(7):1411-20. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22906686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous cholesterol ester hydroperoxides modulate cholesterol levels and inhibit cholesterol uptake in hepatocytes and macrophages.Redox Biol. 2019 Feb;21:101069. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.101069. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30576926 Free PMC article.
-
The expression and functions of toll-like receptors in atherosclerosis.Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:393946. doi: 10.1155/2010/393946. Epub 2010 Jun 24. Mediators Inflamm. 2010. PMID: 20652007 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Krieger M. The other side of scavenger receptors: pattern recognition for host defense. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1997;8:275–280. - PubMed
-
- Miller YI, Chang MK, Binder CJ, Shaw PX, Witztum JL. Oxidized low density lipoprotein and innate immune receptors. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2003;14:437–445. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkbacka H, Kunjathoor VV, Moore KJ, Koehn S, Ordija CM, Lee MA, Means T, Halmen K, Luster AD, Golenbock DT, Freeman MW. Reduced atherosclerosis in MyD88-null mice links elevated serum cholesterol levels to activation of innate immunity signaling pathways. Nat Med. 2004;10:416–421. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

