Conebeam CT of the head and neck, part 2: clinical applications
- PMID: 19461061
- PMCID: PMC7051564
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1654
Conebeam CT of the head and neck, part 2: clinical applications
Abstract
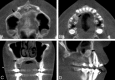
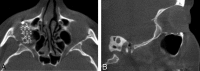
Conebeam x-ray CT (CBCT) is being increasingly used for point-of-service head and neck and dentomaxillofacial imaging. This technique provides relatively high isotropic spatial resolution of osseous structures with a reduced radiation dose compared with conventional CT scans. In this second installment in a 2-part review, the clinical applications in the dentomaxillofacial and head and neck regions will be explored, with particular emphasis on diagnostic imaging of the sinuses, temporal bone, and craniofacial structures. Several controversies surrounding the emergence of CBCT technology will also be addressed.
Figures
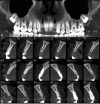
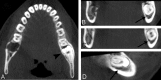
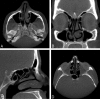
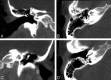
References
-
- Robb RA. The dynamic spatial reconstructor: an x-ray video-fluoroscopic CT scanner for dynamic volume imaging of moving organs. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1982;1:22–33 - PubMed
-
- Saint-Félix D, Trousset Y, Picard C, et al. In vivo evaluation of a new system for 3D computerized angiography. Phys Med Biol 1994;39:583–95 - PubMed
-
- Silver MD, Yahata M, Saito Y, et al. Volume CT of anthropomorphic phantoms using a radiation therapy simulator. In: Shaw R, ed. Medical Imaging VI: Instrumentation: Proceedings of SPIE 1992;1651:197–211
-
- Cho PS, Johnson RH, Griffin TW. Cone-beam CT for radiotherapy applications. Phys Med Biol 1995. :40:1863–83 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
