Control of the rate of evaporation in protein crystallization by the 'microbatch under oil' method
- PMID: 19461852
- PMCID: PMC2553557
- DOI: 10.1107/S0021889808024667
Control of the rate of evaporation in protein crystallization by the 'microbatch under oil' method
Abstract
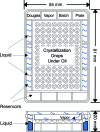
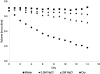
Microbatch crystallization under oil is a powerful procedure for obtaining protein crystals. Using this method, aqueous protein solutions are dispensed under liquid oil, and water evaporates through the layer of oil, with a concomitant increase in the concentrations of both protein and precipitant until the nucleation point is reached. A technique is presented for regulating the rate of water evaporation, which permits fine tuning of the crystallization conditions as well as preventing complete desiccation of the drops in the microbatch crystallization trays.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Compatibility of detergents with the microbatch-under-oil crystallization method.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003 Jun;59(Pt 6):1114-6. doi: 10.1107/s0907444903008175. Epub 2003 May 23. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003. PMID: 12777792
-
Phase diagram and dilution experiments in the crystallization of carboxypeptidase G2.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994 May 1;50(Pt 3):293-7. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993013186. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1994. PMID: 15299442
-
Bound-solvent structures for microgravity-, ground control-, gel- and microbatch-grown hen egg-white lysozyme crystals at 1.8 A resolution.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1999 Apr;55(Pt 4):745-52. doi: 10.1107/s0907444998016047. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1999. PMID: 10089304
-
Modified microbatch and seeding in protein crystallization experiments.J Synchrotron Radiat. 2004 Jan 1;11(Pt 1):24-6. doi: 10.1107/s0909049503023926. Epub 2003 Nov 28. J Synchrotron Radiat. 2004. PMID: 14646125 Review.
-
Comparative studies of protein crystallization by vapour-diffusion and microbatch techniques.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1998 Jan 1;54(Pt 1):8-15. doi: 10.1107/s0907444997005374. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1998. PMID: 9761813 Review.
Cited by
-
Controlled in meso phase crystallization--a method for the structural investigation of membrane proteins.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035458. Epub 2012 Apr 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22536388 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of biological macromolecule crystallization.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 31;14(6):11643-91. doi: 10.3390/ijms140611643. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23727935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Supersaturation-controlled microcrystallization and visualization analysis for serial femtosecond crystallography.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 7;8(1):2541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20899-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29416086 Free PMC article.
-
A simple technique to reduce evaporation of crystallization droplets by using plate lids with apertures for adding liquids.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014 Dec 1;70(Pt 12):1707-13. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X14025126. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014. PMID: 25484231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chayen, N. E. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 198–202.
-
- Chayen, N. E. (1998). Acta Cryst. D54, 8–15. - PubMed
-
- Chayen, N. E., Shaw Stewart, P. D., Maeder, D. L. & Blow, D. M. (1990). J. Appl. Cryst.23, 297–302.
-
- D’Arcy, A., Elmore, C., Stihle, M. & Johnston, J. E. (1996). J. Cryst. Growth, 168, 175–180.
-
- D’Arcy, A., Mac Sweeney, A. & Habera, A. (2004). J. Synchrotron Rad.11, 24–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
