SHRiMP: accurate mapping of short color-space reads
- PMID: 19461883
- PMCID: PMC2678294
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000386
SHRiMP: accurate mapping of short color-space reads
Abstract
The development of Next Generation Sequencing technologies, capable of sequencing hundreds of millions of short reads (25-70 bp each) in a single run, is opening the door to population genomic studies of non-model species. In this paper we present SHRiMP - the SHort Read Mapping Package: a set of algorithms and methods to map short reads to a genome, even in the presence of a large amount of polymorphism. Our method is based upon a fast read mapping technique, separate thorough alignment methods for regular letter-space as well as AB SOLiD (color-space) reads, and a statistical model for false positive hits. We use SHRiMP to map reads from a newly sequenced Ciona savignyi individual to the reference genome. We demonstrate that SHRiMP can accurately map reads to this highly polymorphic genome, while confirming high heterozygosity of C. savignyi in this second individual. SHRiMP is freely available at http://compbio.cs.toronto.edu/shrimp.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

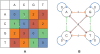

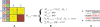
 ) corresponds to the translation currently being used. In the alignment (C) after the sequencing error, the original translation of the read (starting from a T) no longer matches, but a different one (starting from a C) does.
) corresponds to the translation currently being used. In the alignment (C) after the sequencing error, the original translation of the read (starting from a T) no longer matches, but a different one (starting from a C) does.

References
-
- Bowtie. http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

