A method to generate human mesenchymal stem cell-derived neurons which express and are excited by multiple neurotransmitters
- PMID: 19461957
- PMCID: PMC2683550
- DOI: 10.1251/bpo147
A method to generate human mesenchymal stem cell-derived neurons which express and are excited by multiple neurotransmitters
Abstract
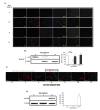
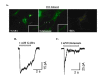
The present study describes a protocol to generate heterogenous populations of neurotransmitter-producing neurons from human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). MSCs are bone marrow (BM)-derived cells which undergo lineage- specific differentiation to generate bone, fat, cartilage and muscle, but are also capable of transdifferentiating into defined ectodermal and endodermal tissues. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the potential of MSCs as an alternative source of customized neurons for experimental neurobiology or other regenerative approaches. Our neuronal protocol utilizes freshly harvested human MSCs cultured on specific surfaces and exposed to an induction cocktail consisting of low serum concentration, retinoic acid (RA), growth factors and supplements. Here we report on the types of neurotransmitters produced by the neurons, and demonstrate that the cells are electrically responsive to exogenous neurotransmitter administration.
Keywords: Gamma-aminobutyric acid; Mesenchymal stem cells.
Figures



References
-
- Korecka JA, Verhaagen J, Hol EM. Cell-replacement and gene-therapy strategies for Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease. Regen Med. 2007;2:425–446. - PubMed
-
- Silani V, Corbo M. Cell-replacement therapy with stem cells in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2004;1:283–289. - PubMed
-
- Kocher AA, Schlechta B, Gasparovicova A, Wolner E, Bonaros N, Laufer G. Stem cells and cardiac regeneration. Transpl Int. 2007;20:731–746. - PubMed
-
- Lock LT, Tzanakakis ES. Stem/Progenitor cell sources of insulin-producing cells for the treatment of diabetes. Tissue Eng. 2007;13:1399–1412. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

