Polycomb mediated epigenetic silencing and replication timing at the INK4a/ARF locus during senescence
- PMID: 19462008
- PMCID: PMC2680618
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005622
Polycomb mediated epigenetic silencing and replication timing at the INK4a/ARF locus during senescence
Abstract
Background: The INK4/ARF locus encodes three tumor suppressor genes (p15(Ink4b), Arf and p16(Ink4a)) and is frequently inactivated in a large number of human cancers. Mechanisms regulating INK4/ARF expression are not fully characterized.
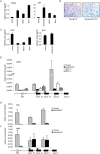
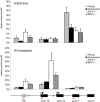
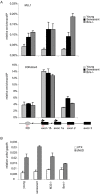
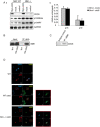
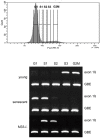
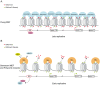
Principal findings: Here we show that in young proliferating embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) member EZH2 together with PRC1 members BMI1 and M33 are strongly expressed and localized at the INK4/ARF regulatory domain (RD) identified as a DNA replication origin. When cells enter senescence the binding to RD of both PRC1 and PRC2 complexes is lost leading to a decreased level of histone H3K27 trimethylation (H3K27me3). This loss is accompanied with an increased expression of the histone demethylase Jmjd3 and with the recruitment of the MLL1 protein, and correlates with the expression of the Ink4a/Arf genes. Moreover, we show that the Polycomb protein BMI1 interacts with CDC6, an essential regulator of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Finally, we demonstrate that Polycomb proteins and associated epigenetic marks are crucial for the control of the replication timing of the INK4a/ARF locus during senescence.
Conclusions: We identified the replication licencing factor CDC6 as a new partner of the Polycomb group member BMI1. Our results suggest that in young cells Polycomb proteins are recruited to the INK4/ARF locus through CDC6 and the resulting silent locus is replicated during late S-phase. Upon senescence, Jmjd3 is overexpressed and the MLL1 protein is recruited to the locus provoking the dissociation of Polycomb from the INK4/ARF locus, its transcriptional activation and its replication during early S-phase. Together, these results provide a unified model that integrates replication, transcription and epigenetics at the INK4/ARF locus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Campisi J. Cancer, aging and cellular senescence. In Vivo. 2000;14:183–188. - PubMed
-
- Dimri GP, Campisi J. Molecular and cell biology of replicative senescence. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1994;59:67–73. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ, DePinho RA. Cellular senescence: mitotic clock or culture shock? Cell. 2000;102:407–410. - PubMed
-
- Core N, Joly F, Boned A, Djabali M. Disruption of E2F signaling suppresses the INK4a-induced proliferative defect in M33-deficient mice. Oncogene. 2004;23:7660–7668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

