Dexamethasone decreases the transmesothelial electrical resistance of the parietal and visceral pleura
- PMID: 19462220
- PMCID: PMC10717257
- DOI: 10.1007/s12576-009-0042-x
Dexamethasone decreases the transmesothelial electrical resistance of the parietal and visceral pleura
Abstract
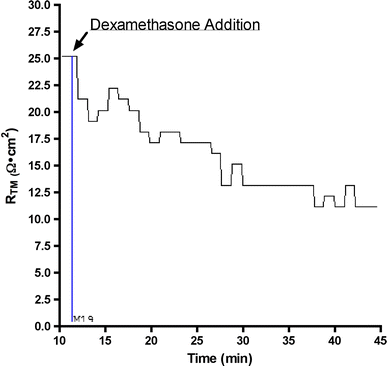
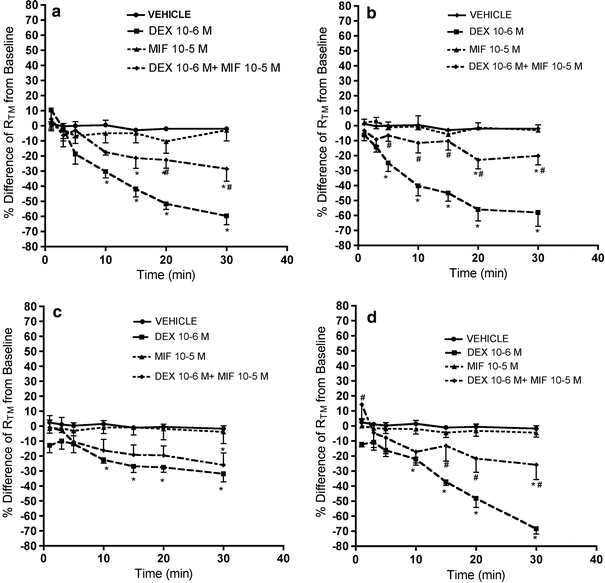
The effect of dexamethasone on the transmesothelial electrical resistance (R(TM)) of sheep pleura was investigated by Ussing chamber experiments. Our results show that dexamethasone decreases the R(TM) of sheep pleurae, in part by stimulation of glucocorticoid receptors. This finding may be of importance in regard to the faster resolution of corticosteroid-treated pleural effusions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
mu-Opioid influence on transmesothelial resistance of isolated sheep pleura and parietal pericardium.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Jan 20;530(3):276-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.11.050. Epub 2006 Jan 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16405886
-
Effect of adrenaline on transmesothelial resistance of isolated sheep pleura.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006 Feb 28;150(2-3):165-72. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2005.04.006. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16476653
-
Effect of amiloride in human and sheep parietal pleura.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2002 Aug 30;132(2):233-7. doi: 10.1016/s1569-9048(02)00077-0. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 12161335
-
[Structure and physiology of the pleura and the pleural space].Rev Pneumol Clin. 2006 Apr;62(2):73-7. doi: 10.1016/s0761-8417(06)75419-0. Rev Pneumol Clin. 2006. PMID: 16670659 Review. French.
-
Anatomy and physiology of the pleural space.Chest Surg Clin N Am. 1994 Aug;4(3):391-403. Chest Surg Clin N Am. 1994. PMID: 7953475 Review.
Cited by
-
Dexamethasone acutely accelerates pleural fluid absorption in mice hydrothoraces.J Physiol Sci. 2010 Jul;60(4):299-302. doi: 10.1007/s12576-010-0089-8. Epub 2010 Apr 10. J Physiol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20383620 Free PMC article.
-
Permeability of the arachnoid and pia mater. The role of ion channels in the leptomeningeal physiology.Childs Nerv Syst. 2012 Apr;28(4):533-40. doi: 10.1007/s00381-012-1688-x. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Childs Nerv Syst. 2012. PMID: 22252717
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

