Implication of chromosome 13 on hypertension and associated disorders in Lyon hypertensive rats
- PMID: 19462495
- PMCID: PMC2915542
- DOI: 10.1097/hjh.0b013e328329e4c0
Implication of chromosome 13 on hypertension and associated disorders in Lyon hypertensive rats
Abstract
Background: Hypertension and associated disorders are major risk factors for cardiovascular disease. The Lyon hypertensive rat (LH) is a genetically hypertensive strain that exhibits spontaneous and salt-sensitive hypertension, exaggerated proteinuria, high body weight, hyperlipidemia, and elevated insulin-to-glucose ratio. Previous genetic mapping identified quantitative trait loci (QTLs) influencing blood pressure (BP) on rat chromosome 13 (RNO13) in several models of hypertension.
Methods: To study the effects of a single chromosome on the mapped traits, we generated consomic strains by substituting LH RNO13 with that of the normotensive Brown Norway (BN) strain (LH-13BN) and reciprocal consomics by substituting a BN RNO13 with that of LH (BN-13LH). These reciprocal consomic strains, as well as the two parental strains were characterized for BP, metabolic and morphological parameters.
Results: Compared with LH parents, LH-13BN rats showed decreased mean BP (up to -24 mmHg on 2% NaCl in the drinking water), urine proteins and lipids, and increased body weight. Differences between BN-13LH and BN rats were much smaller than those observed between LH-13BN and LH rats, demonstrating the effects of the highly resistant BN genome background. Plasma renin activity was not affected by the substitution of RNO13, despite the significant BP differences.
Conclusion: The present work demonstrates that RNO13 is a determinant of BP, proteinuria, and plasma lipids in the LH rat. The distinct phenotypic differences between the consomic LH-13BN and the LH make it a powerful model to determine genes and pathways leading to these risk factors for cardiovascular and renal disease.
Figures
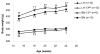

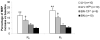
Comment in
-
Opportunities and limitations of genetic analysis of hypertensive rat strains.J Hypertens. 2009 Jun;27(6):1129-33. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832bb832. J Hypertens. 2009. PMID: 19454904 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
[Importance of chromosome 17 in genetically hypertensive rats of the Lyon strain (LH): study of a consomic strain].Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2007 Aug;100(8):709-13. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2007. PMID: 17928782 French.
-
Effects of chromosome 17 on features of the metabolic syndrome in the Lyon hypertensive rat.Physiol Genomics. 2008 Apr 22;33(2):212-7. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00262.2007. Epub 2008 Feb 19. Physiol Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18285521
-
Dissection of chromosome 18 blood pressure and salt-sensitivity quantitative trait loci in the spontaneously hypertensive rat.Hypertension. 2009 Sep;54(3):639-45. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.126664. Epub 2009 Jul 20. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19620519 Free PMC article.
-
SHR.BN-congenic strains for genetic analysis of multifactorially determined traits.Folia Biol (Praha). 2000;46(1):25-9. Folia Biol (Praha). 2000. PMID: 10730879 Review.
-
Use of recombinant inbred strains for evaluation of intermediate phenotypes in spontaneous hypertension.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1994 Nov;21(11):903-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1994.tb02463.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1994. PMID: 7882582 Review.
Cited by
-
Opportunities and limitations of genetic analysis of hypertensive rat strains.J Hypertens. 2009 Jun;27(6):1129-33. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832bb832. J Hypertens. 2009. PMID: 19454904 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Rat chromosome 8 confers protection against dyslipidemia caused by a high-fat/low-carbohydrate diet.J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. 2012;5(2):81-93. doi: 10.1159/000338848. Epub 2012 Jun 19. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. 2012. PMID: 22722880 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional profiling in rat hair follicles following simulated Blast insult: a new diagnostic tool for traumatic brain injury.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 19;9(8):e104518. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104518. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25136963 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic structure of nucleotide diversity among Lyon rat models of metabolic syndrome.BMC Genomics. 2014 Mar 14;15(1):197. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-197. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24628878 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial polymorphisms in rat genetic models of hypertension.Mamm Genome. 2010 Jun;21(5-6):299-306. doi: 10.1007/s00335-010-9259-5. Epub 2010 May 5. Mamm Genome. 2010. PMID: 20443117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ong KL, Cheung BM, Man YB, Lau CP, Lam KS. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among United States adults 1999-2004. Hypertension. 2007;49:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Cowley AW., Jr Genomics and homeostasis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003;284:R611–27. - PubMed
-
- Dupont J, Dupont JC, Froment A, Milon H, Vincent M. Selection of three strains of rats with spontaneously different levels of blood pressure. Biomedicine. 1973;19:36–41. - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM. Insulin and hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1990;12:803–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

