Novelty modulates the stimulating motor effects of ethanol in preweanling rats
- PMID: 19463258
- PMCID: PMC2703475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2009.01.012
Novelty modulates the stimulating motor effects of ethanol in preweanling rats
Abstract
During early ontogeny heterogeneous rats are sensitive to ethanol's stimulating effects. In adulthood locomotor activity in a novel environment is a valuable predictor of acute sensitivity to the activating effects of various drugs, including ethanol. Environmental novelty modulates response to ethanol and other drugs in adult rats. The present study analyzed the role of novelty in the acute locomotor response induced by ethanol earlier in development, during the preweanling period, a stage characterized by enhanced sensitivity to ethanol's reinforcing effects. In Experiment 1 we evaluated the predictive value of baseline locomotor activity upon ethanol-induced locomotor effects in 12-day-old rats. In Experiment 2 we tested whether repeated familiarization with the testing environment would reduce the stimulating effects induced by ethanol on postnatal day 12. Individual differences in response to an inescapable novel environment significantly predicted the locomotor activating effects of ethanol, but not other acute effects of the drug, such as hypothermia, motor impairment or sedation. Behavioral activation induced by ethanol during the preweanling period was attenuated after familiarization with the testing environment, suggesting that environmental novelty is critical for activating effects of ethanol.
Figures
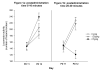
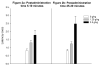
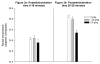
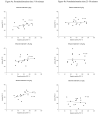
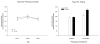
References
-
- Arias C, Chotro MG. Ethanol-induced preferences or aversions as a function of age in preweanling rats. Behav Neurosci. 2006;120(3) - PubMed
-
- Arias C, Mlewski EC, Molina JC, Spear NE. Naloxone and Baclofen attenuate ethanol’s locomotor-activating effects in preweanling Sprague-Dawley rats. Behavl Neurosci (in press) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 MH035219/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AA11960/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- F31AA017339/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011960/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA013098/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH035219/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH035219/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AA015992/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013098/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA015992/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA017823/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA006634/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA010223/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AA017339/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

