Antegrade percutaneous closure of membranous ventricular septal defect using X-ray fused with magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 19463430
- PMCID: PMC2698297
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcin.2008.09.014
Antegrade percutaneous closure of membranous ventricular septal defect using X-ray fused with magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Objectives: We hypothesized that X-ray fused with magnetic resonance imaging (XFM) roadmaps might permit direct antegrade crossing and delivery of a ventricular septal defect (VSD) closure device and thereby reduce procedure time and radiation exposure.
Background: Percutaneous device closure of membranous VSD is cumbersome and time-consuming. The procedure requires crossing the defect retrograde, snaring and exteriorizing a guidewire to form an arteriovenous loop, then delivering antegrade a sheath and closure device.
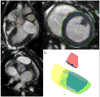
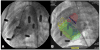
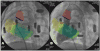
Methods: Magnetic resonance imaging roadmaps of cardiac structures were obtained from miniature swine with spontaneous VSD and registered with live X-ray using external fiducial markers. We compared antegrade XFM-guided VSD crossing with conventional retrograde X-ray-guided crossing for repair.
Results: Antegrade XFM crossing was successful in all animals. Compared with retrograde X-ray, antegrade XFM was associated with shorter time to crossing (167 +/- 103 s vs. 284 +/- 61 s; p = 0.025), shorter time to sheath delivery (71 +/- 32 s vs. 366 +/- 145 s; p = 0.001), shorter fluoroscopy time (158 +/- 95 s vs. 390 +/- 137 s; p = 0.003), and reduced radiation dose-area product (2,394 +/- 1,522 mG.m(2) vs. 4,865 +/- 1,759 mG.m(2); p = 0.016).
Conclusions: XFM facilitates antegrade access to membranous VSD from the right ventricle in swine. The simplified procedure is faster and reduces radiation exposure compared with the conventional retrograde approach.
Figures

References
-
- Minette MS, Sahn DJ. Ventricular septal defects. Circulation. 2006;114:2190–7. - PubMed
-
- Carminati M, Butera G, Chessa M, et al. Transcatheter closure of congenital ventricular septal defects: results of the European Registry. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2361–8. - PubMed
-
- Mullins CE. Cardiac catheterization in congenital heart disease: pediatric and adult. Malden, Mass.: Blackwell Futura; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

