Metabolic memory in diabetes - from in vitro oddity to in vivo problem: role of apoptosis
- PMID: 19463916
- PMCID: PMC3021362
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2009.05.006
Metabolic memory in diabetes - from in vitro oddity to in vivo problem: role of apoptosis
Abstract
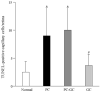
Retinal capillary cells undergo apoptosis before pathology characteristic of retinopathy can be observed, and the appearance of apoptotic capillary cell can predict the development of pathology. The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of reversal of hyperglycemia on retinal capillary cell apoptosis, and identify the apoptosis encoding genes. Streptozotocin-diabetic rats were maintained either in poor glycemic control (PC, glycated hemoglobin, GHb >11%) or in good glycemic control (GC, GHb <6%) for 12 months, or allowed to be in PC for 6 months followed by GC for 6 additional months (PC-GC). Capillary cell apoptosis was determined in the trypsin-digested retinal microvasculature by TUNEL staining, and the genes encoding apoptosis were identified by Oligo GEArray rat apoptosis microarray that profiles 113 genes. Six months of good glycemic control that followed 6 months of poor control failed to attenuate the number of TUNEL-positive capillary cells in the retinal microvasculature. Twenty-three retinal genes, mainly from TNF ligand and receptor, caspase, Bcl-2 and death domain subfamilies that were upregulated by least a two-fold in PC rats remain upregulated after reversal of hyperglycemia. Thus, the continued activation of apoptosis plays a major role in the resistance of retinopathy to halt after re-institution of good glycemic control, and the regulation apoptosis machinery could help retard the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs Renu A. Kowluru and Pooi-see Chan have no financial, personal or other relationship with other people or organizations within three years of beginning the work submitted that could inappropriately influence (bias) their work.
Figures
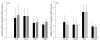
Similar articles
-
Metabolic memory phenomenon and accumulation of peroxynitrite in retinal capillaries.Exp Diabetes Res. 2007;2007:21976. doi: 10.1155/2007/21976. Exp Diabetes Res. 2007. PMID: 17641740 Free PMC article.
-
Re-institution of good metabolic control in diabetic rats and activation of caspase-3 and nuclear transcriptional factor (NF-kappaB) in the retina.Acta Diabetol. 2004 Dec;41(4):194-9. doi: 10.1007/s00592-004-0165-8. Acta Diabetol. 2004. PMID: 15660203
-
Resistance of retinal inflammatory mediators to suppress after reinstitution of good glycemic control: novel mechanism for metabolic memory.J Diabetes Complications. 2010 Jan-Feb;24(1):55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2008.10.002. Epub 2008 Dec 3. J Diabetes Complications. 2010. PMID: 19056300 Free PMC article.
-
Role of histone acetylation in the development of diabetic retinopathy and the metabolic memory phenomenon.J Cell Biochem. 2010 Aug 15;110(6):1306-13. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22644. J Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20564224 Free PMC article.
-
[Retinal neuronal cell death: molecular mechanism and neuroprotection].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001 Dec;105(12):884-902. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11802459 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic modification of Sod2 in the development of diabetic retinopathy and in the metabolic memory: role of histone methylation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Jan 14;54(1):244-50. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10854. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23221071 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic changes in mitochondrial superoxide dismutase in the retina and the development of diabetic retinopathy.Diabetes. 2011 Apr;60(4):1304-13. doi: 10.2337/db10-0133. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21357467 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic retinopathy, superoxide damage and antioxidants.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011 Mar 1;12(3):352-61. doi: 10.2174/138920111794480507. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20939803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Changes in Endothelial Progenitors as a Possible Cellular Basis for Glycemic Memory in Diabetic Vascular Complications.J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:436879. doi: 10.1155/2015/436879. Epub 2015 May 28. J Diabetes Res. 2015. PMID: 26106624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF) protects against retinal cell apoptosis and preserves visual behavior in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Aug 30;24(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04614-y. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39215295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brownlee M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 2005;54:1615–1625. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Goeddel DV. TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science. 2002;296:1634–1635. - PubMed
-
- Chen QM, Tu VC. Apoptosis and heart failure: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2002;2:43–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

