Forkhead box transcription factor O1 inhibits cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase in human hepatocytes and in high fat diet-fed mice
- PMID: 19463968
- PMCID: PMC2743791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.05.004
Forkhead box transcription factor O1 inhibits cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase in human hepatocytes and in high fat diet-fed mice
Abstract
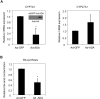
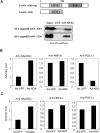
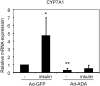
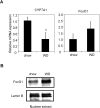
The conversion of cholesterol to bile acids is the major pathway for cholesterol catabolism. Bile acids are metabolic regulators of triglycerides and glucose metabolism in the liver. This study investigated the roles of FoxO1 in the regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) gene expression in primary human hepatocytes. Adenovirus-mediated expression of a phosphorylation defective and constitutively active form of FoxO1 (FoxO1-ADA) inhibited CYP7A1 mRNA expression and bile acid synthesis, while siRNA knockdown of FoxO1 resulted in a approximately 6-fold induction of CYP7A1 mRNA in human hepatocytes. Insulin caused rapid exclusion of FoxO1 from the nucleus and resulted in the induction of CYP7A1 mRNA expression, which was blocked by FoxO1-ADA. In high fat diet-fed mice, CYP7A1 mRNA expression was repressed and inversely correlated to increase hepatic FoxO1 mRNA expression and FoxO1 nuclear retention. In conclusion, our current study provides direct evidence that FoxO1 is a strong repressor of CYP7A1 gene expression and bile acid synthesis. Impaired regulation of FoxO1 may cause down-regulation of CYP7A1 gene expression and contribute to dyslipidemia in insulin resistance.
Figures
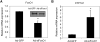
Similar articles
-
Insulin-dependent suppression of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase is a possible link between glucose and cholesterol metabolisms.Exp Mol Med. 2011 Oct 31;43(10):571-9. doi: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.10.064. Exp Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21817852 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase expression in human hepatocytes: roles of forkhead box O1 and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 29;281(39):28745-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605815200. Epub 2006 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16885156 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-185 modulates CYP7A1 mediated cholesterol-bile acid metabolism through post-transcriptional and post-translational regulation of FoxO1.Atherosclerosis. 2022 May;348:56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.03.007. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Atherosclerosis. 2022. PMID: 35287950
-
A GAPDH-mediated trans-nitrosylation pathway is required for feedback inhibition of bile salt synthesis in rat liver.Gastroenterology. 2014 Nov;147(5):1084-93. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.07.030. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 25066374
-
The pharmacological exploitation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase, the key enzyme in bile acid synthesis: from binding resins to chromatin remodelling to reduce plasma cholesterol.Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Dec;116(3):449-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.08.003. Epub 2007 Sep 7. Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17959250 Review.
Cited by
-
High-resolution genetic mapping using the Mouse Diversity outbred population.Genetics. 2012 Feb;190(2):437-47. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.132597. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22345611 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO transcription factors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Liver Res. 2017 Sep;1(3):168-173. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2017.11.004. Liver Res. 2017. PMID: 30034912 Free PMC article.
-
Paternal High-Fat Diet Altered Sperm 5'tsRNA-Gly-GCC Is Associated With Enhanced Gluconeogenesis in the Offspring.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Apr 11;9:857875. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.857875. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35480893 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor α regulates diurnal rhythm and fasting induction of sterol 12α-hydroxylase in bile acid synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 27;288(52):37154-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.485987. Epub 2013 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24226095 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-dependent suppression of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase is a possible link between glucose and cholesterol metabolisms.Exp Mol Med. 2011 Oct 31;43(10):571-9. doi: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.10.064. Exp Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21817852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiang JY. Regulation of bile acid synthesis: pathways, nuclear receptors, and mechanisms. J Hepatol. 2004;40:539–551. - PubMed
-
- Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa JJ, Tu H, Learned RM, Luk A, Hull MV, Lustig KD, Mangelsdorf DJ, Shan B. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science. 1999;284:1362–1365. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin B, Jones SA, Price RR, Watson MA, McKee DD, Moore LB, Galardi C, Wilson JG, Lewis MC, Roth ME, Maloney PR, Willson TM, Kliewer SA. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol Cell. 2000;6:517–526. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L, Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Luo G, Jones SA, Goodwin B, Richardson JA, Gerard RD, Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA. Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005;2:217–225. - PubMed
-
- Miyake JH, Wang SL, Davis RA. Bile acid induction of cytokine expression by macrophages correlates with repression of hepatic cholesterol 7alphahydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:21805–21808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

