[Metformin also as first choice in patients with normal weight. Has its use increased?]
- PMID: 19464082
- PMCID: PMC7022010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aprim.2008.10.010
[Metformin also as first choice in patients with normal weight. Has its use increased?]
Abstract
Objective: To assess whether the release of the new consensus algorithms in August 2006, along with the consensus recommendation of also using metformin as first choice in patients with normal weight, has led to an increase in the use of this drug in the period immediately after.
Design: Retrospective longitudinal Study. SITES: Santiago de Compostela Health District (A Coruña).
Participants: Users of the Galician health service in the Santiago de Compostela Health District.
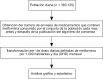
Methods: The evolution of the monthly number of DHD (Daily Defined Doses/1000 inhabitants/day) of metformin from early 2003 until 12 months after the issuing of new algorithms was analysed graphically and using a multiple regression model.
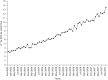
Results: The graphical representation of the DHD of metformin over time shows a linear growth for the period, but there is an increasing trend after the publication of the new consensus algorithm. The multiple regression showed that the increase is statistically significant.
Conclusions: Following the publication of the new consensus algorithm an increasing trend in the use of metformin is observed in the short term.
Objetivo: Evaluar si tras la publicación en agosto de 2006 de los nuevos algoritmos de consenso con la recomendación de utilizar metformina de elección también en pacientes con normopeso se ha producido un aumento en la utilización de este medicamento en el periodo inmediatamente posterior.
Diseño: Estudio longitudinal-retrospectivo.
Emplazamiento: Área Sanitaria de Santiago de Compostela, A Coruña.
Participantes: usuarios del Servicio Gallego de Salud en el Área Sanitaria de Santiago de Compostela.
Métodos: Se estudia la evolución de las dosis diarias definidas/1.000 habitantes/día (DHD) mensuales de metformina desde principios de 2003 hasta 12 meses después de la publicación de los nuevos algoritmos, analizando los datos gráficamente y mediante un modelo de regresión múltiple.
Resultado: La representación gráfica de la serie temporal de las DHD de metformina muestra un crecimiento lineal para el periodo, y se aprecia aumento de la tendencia de crecimiento tras la publicación del nuevo algoritmo de consenso. La regresión múltiple muestra que el aumento es estadísticamente significativo.
Conclusiones: Tras la publicación de los nuevos algoritmos de consenso, se observa a corto plazo un aumento de la tendencia de crecimiento en la utilización de metformina.
Figures
References
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34) Lancet. 1998;352:854–865. - PubMed
-
- Ong C.R., Molyneaux L.M., Constantino M.I., Twigg S.M., Yue D.K. Long-term efficacy of metformin therapy in nonobese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2361–2364. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly L.A., Doney A.S., Hattersley A.T., Morris A.D., Pearson E.R. The effect of obesity on glycaemic response to metformin or sulphonylureas in Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2006;23:128–133. - PubMed
-
- Nathan D.M., Buse J.B., Davidson M.B., Heine R.J., Holman R.R., Sherwin R. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1963–1972. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical