M-LDH physically associated with sarcolemmal K ATP channels mediates cytoprotection in heart embryonic H9C2 cells
- PMID: 19464385
- PMCID: PMC2758067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.05.012
M-LDH physically associated with sarcolemmal K ATP channels mediates cytoprotection in heart embryonic H9C2 cells
Abstract
Muscle form of lactate dehydrogenase (M-LDH) physically associate with K(ATP) channel subunits, Kir6.2 and SUR2A, and is an integral part of the ATP-sensitive K(+) (K(ATP)) channel protein complex in the heart. Here, we have shown that concomitant introduction of viral constructs containing truncated and mutated forms of M-LDH (Delta M-LDH) and 193gly-M-LDH respectively, generate a phenotype of rat heart embryonic H9C2 cells that do not contain functional M-LDH as a part of the K(ATP) channel protein complex. The K(+) current was increased in wild type cells, but not in cells expressing Delta M-LDH/193gly-M-LDH, when they were exposed to chemical hypoxia induced by 2,4 dinitrophenol (DNP; 10mM). At the same time, the outcome of chemical hypoxia was much worse in Delta M-LDH/193gly-M-LDH phenotype than in the control one, and that was associated with increased loss of intracellular ATP in cells infected with Delta M-LDH/193gly-M-LDH. On the other hand, cells expressing Kir6.2AFA, a Kir6.2 mutant that abolishes K(ATP) channel conductance without affecting intracellular ATP levels, survived chemical hypoxia much better than cells expressing Delta M-LDH/193gly-M-LDH. Based on the obtained results, we conclude that M-LDH physically associated with Kir6.2/SUR2A regulates the activity of sarcolemmal K(ATP) channels as well as an intracellular ATP production during metabolic stress, both of which are important for cell survival.
Figures


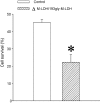
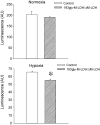
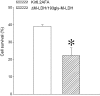
References
-
- Brady P.A., Zhang S., Lopez J.R., Jovanović A., Alekseev A.E., Terzic A. Dual effect of glyburide, an antagonist of KATP channels, on metabolic inhibition-induced Ca2+ loading in cardiomyocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996;308:343–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S18744/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 059528/Z/99/Z/JMW/CP/JF/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- PG/08/106/26155/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/04/086/17410/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0400608/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

