Replication and conjugative mobilization of broad host-range IncQ plasmids
- PMID: 19465049
- PMCID: PMC2752045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2009.05.001
Replication and conjugative mobilization of broad host-range IncQ plasmids
Abstract
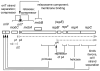
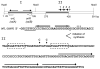
The IncQ plasmids have a broader host-range than any other known replicating element in bacteria. Studies on the replication and conjugative mobilization of these plasmids, which have mostly been focused on the nearly identical RSF1010 and R1162, are summarized with a view to understanding how this broad host-range is achieved. Several significant features of IncQ plasmids emerge from these studies: (1) initiation of replication, involving DnaA-independent activation of the origin and a dedicated primase, is strictly host-independent. (2) The plasmids can be conjugatively mobilized by a variety of different type IV transporters, including those engaged in the secretion of proteins involved in pathogenesis. (3) Stability is insured by a combination of high copy-number and modulated gene expression to reduce metabolic load.
Figures




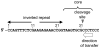
References
-
- Bagdasarian M, Lurz R, Rückert B, Franklin FC, Bagdasarian MM, Frey J, Timmis KN. Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981;16:237–247. - PubMed
-
- Bagdasarian M, Bagdasarian M, Lurz R, Nordheim A, Frey J, Timmis K. Molecular and functional analysis of the broad host range plasmid RSF1010 and construction of vectors for gene cloning in gram-negative bacteria. In: Mitsuhashi S, editor. Drug Resistance in Bacteria. New York: Thieme-Stratton; 1982. pp. 183–197.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

