C/EBP{alpha} is required for pulmonary cytoprotection during hyperoxia
- PMID: 19465518
- PMCID: PMC2742785
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00094.2009
C/EBP{alpha} is required for pulmonary cytoprotection during hyperoxia
Abstract
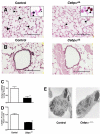
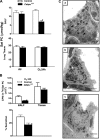
A number of transcriptional pathways regulating fetal lung development are active during repair of the injured lung. We hypothesized that C/EBPalpha, a transcription factor critical for lung maturation, plays a role in protection of the alveolar epithelium following hyperoxic injury of the mature lung. Transgenic Cebpalpha(Delta/Delta) mice, in which Cebpalpha was conditionally deleted from Clara cells and type II cells after birth, were developed. While no pulmonary abnormalities were observed in the Cebpalpha(Delta/Delta) mice (7-8 wk old) under normal conditions, the mice were highly susceptible to hyperoxia. Cebpalpha(Delta/Delta) mice died within 4 days of exposure to 95% oxygen in association with severe lung inflammation, altered maturation of surfactant protein B and C, decreased surfactant lipid secretion, and abnormal lung mechanics at a time when all control mice survived. mRNA microarray analysis of isolated type II cells at 0, 2, and 24 h of hyperoxia demonstrated the reduced expression of number of genes regulating surfactant lipid and protein homeostasis, including Srebf, Scap, Lpcat1, Abca3, Sftpb, and Napsa. Genes influencing cell signaling or immune responses were induced in the lungs of Cebpalpha(Delta/Delta) mice. C/EBPalpha was required for the regulation of genes associated with surfactant lipid homeostasis, surfactant protein biosynthesis, processing and transport, defense response to stress, and cell redox homeostasis during exposure to hyperoxia. While C/EBPalpha did not play a critical role in postnatal pulmonary function under normal conditions, C/EBPalpha mediated protection of the lung during acute lung injury induced by hyperoxia.
Figures

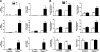
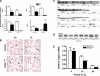



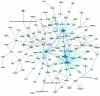
 B indicates binding; A → B indicates A is the cause of B; A
B indicates binding; A → B indicates A is the cause of B; A B indicates A inhibits B, and
B indicates A inhibits B, and  indicates self-regulation. The mRNA expression of cluster 3 genes was negatively correlated with the length of hyperoxia exposure time and color coded in green. Positively correlated genes are color coded in pink. Many genes in the network were known to be involved in synthesis, processing, and regulation of surfactant proteins and lipids.
indicates self-regulation. The mRNA expression of cluster 3 genes was negatively correlated with the length of hyperoxia exposure time and color coded in green. Positively correlated genes are color coded in pink. Many genes in the network were known to be involved in synthesis, processing, and regulation of surfactant proteins and lipids.
Similar articles
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α regulates the protease/antiprotease balance required for bronchiolar epithelium regeneration.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Oct;47(4):454-63. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0239OC. Epub 2012 May 31. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22652201 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing hyperoxia-induced C/EBPα in neonatal mice improves lung architecture via enhanced proliferation of alveolar epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Aug;301(2):L187-96. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00082.2011. Epub 2011 May 13. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21571903 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional deletion of Abca3 in alveolar type II cells alters surfactant homeostasis in newborn and adult mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):L646-59. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00409.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20190032 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of surfactant protein gene expression by hyperoxia in the lung.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004 Feb;6(1):185-90. doi: 10.1089/152308604771978499. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004. PMID: 14713350 Review.
-
Surfactant protein B deficiency worsens hyperoxic injury to the alveolar epithelium.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999 Oct;21(4):449-50. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.21.4.f166. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10502553 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α regulates the protease/antiprotease balance required for bronchiolar epithelium regeneration.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Oct;47(4):454-63. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0239OC. Epub 2012 May 31. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22652201 Free PMC article.
-
LKB1 drives stasis and C/EBP-mediated reprogramming to an alveolar type II fate in lung cancer.Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 28;13(1):1090. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28619-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35228570 Free PMC article.
-
Sumoylation of CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein α inhibits lung differentiation in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia model rats.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jun;24(12):7067-7071. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15310. Epub 2020 May 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32363643 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NRF2 in immune modulator expression in developing lung.FASEB J. 2021 Aug;35(8):e21758. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100129RR. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34245611 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Stem Cells: Emergent Nature of Tumor Emergency.Front Genet. 2018 Nov 16;9:544. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00544. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30505319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreani M, Olivier JL, Berenbaum F, Raymondjean M, Bereziat G. Transcriptional regulation of inflammatory secreted phospholipases A(2). Biochim Biophys Acta 1488: 149–158, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett GR Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem 234: 466–468, 1959. - PubMed
-
- Berg T, Didon L, Nord M. Ectopic expression of C/EBPalpha in the lung epithelium disrupts late lung development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 291: L683–L693, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Berruyer C, Pouyet L, Millet V, Martin FM, LeGoffic A, Canonici A, Garcia S, Bagnis C, Naquet P, Galland F. Vanin-1 licenses inflammatory mediator production by gut epithelial cells and controls colitis by antagonizing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activity. J Exp Med 203: 2817–2827, 2006. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

