Transmural pressure and axial loading interactively regulate arterial remodeling ex vivo
- PMID: 19465545
- PMCID: PMC2711737
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00972.2008
Transmural pressure and axial loading interactively regulate arterial remodeling ex vivo
Abstract
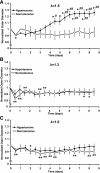
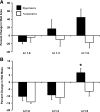
Physiological axial strains range between 40 and 60% in arteries, resulting in stresses comparable to those due to normal blood pressure or flow. To investigate the contribution of axial strain to arterial remodeling and function, porcine carotid arteries were cultured for 9 days at physiological and reduced axial stretch ratios in the presence of normotensive and hypertensive transmural pressures by ex vivo perfusion techniques. Consistent with previous in vivo studies, vessels cultured with physiological levels of axial strain and exposed to hypertensive pressure had greater mass, wall area, and outer diameter relative to those cultured at the same axial stretch ratio and normotensive pressure. Reducing the amount of axial strain resulted in mass loss and decreased cell proliferation. Culture in a hypertensive pressure environment at reduced axial strain produced arteries with greater contractility in response to norepinephrine. Arteries cultured at reduced axial strain with the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor GM6001 maintained their masses over culture, indicating a possible mechanism for this model of axial stretch-dependent remodeling. Although not historically considered one of the primary stimuli for remodeling, multiple linear regression analysis revealed that axial strain had an impact similar to or greater than transmural pressure on various remodeling indexes (i.e., outer diameter, wall area, and wet mass), suggesting that axial strain is a primary mediator of vascular remodeling.
Figures



References
-
- Bardy N, Karillon GJ, Merval R, Samuel JL, Tedgui A. Differential effects of pressure and flow on DNA and protein synthesis and on fibronectin expression by arteries in a novel organ culture system. Circ Res 77: 684–694, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Chesler NC, Ku DN, Galis ZS. Transmural pressure induces matrix-degrading activity in porcine arteries ex vivo. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 277: H2002–H2009, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Chironi G, Gariepy J, Denarie N, Balice M, Megnien JL, Levenson J, Simon A. Influence of hypertension on early carotid artery remodeling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23: 1460–1464, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Chuong CJ, Fung YC. On residual stresses in arteries. J Biomech Eng 108: 189–192, 1986. - PubMed
-
- Clerin V, Gusic RJ, O'Brien J, Kirshbom PM, Myung RJ, Gaynor JW, Gooch KJ. Mechanical environment, donor age, and presence of endothelium interact to modulate porcine artery viability ex vivo. Ann Biomed Eng 30: 1117–1127, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

