Expression of retinoic acid receptor alpha in the germline is essential for proper cellular association and spermiogenesis during spermatogenesis
- PMID: 19465599
- PMCID: PMC2685727
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.020040
Expression of retinoic acid receptor alpha in the germline is essential for proper cellular association and spermiogenesis during spermatogenesis
Abstract
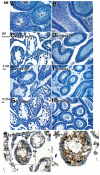
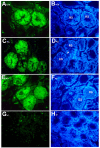
Signaling through vitamin A metabolites is indispensable for spermatogenesis, and disruption of retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARalpha) function resulted in male sterility and aberrant spermatogenesis, which resembled vitamin A deficiency. Here we investigated the lineage- and cell-specific role of RARalpha-mediated signaling during spermatogenesis using germ-cell transplantation and genetically manipulated mouse models. We demonstrated that RARalpha-deficient germ-cell stem cells were able to repopulate germ-cell-depleted wild-type testes and initiate spermatogenesis; however, improper cellular associations and abnormal sperm formation were observed. We further generated RARalpha-deficient mice that expressed RARalpha-EGFP fusion protein uniquely in haploid germ cells. Strikingly, spermatid orientation, alignment and release, as well as sperm morphology, were normal and there was a partial rescue of sterility. These data provide the first direct evidence for a distinct requirement of RARalpha-mediated retinoid signaling specifically in germ cells.
Figures
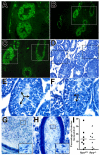
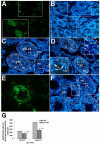
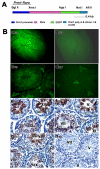

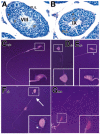
References
-
- Akmal, K. M., Dufour, J. M. and Kim, K. H. (1997). Retinoic acid receptor alpha gene expression in the rat testis: potential role during the prophase of meiosis and in the transition from round to elongating spermatids. Biol. Reprod. 56, 549-556. - PubMed
-
- Akmal, K. M., Dufour, J. M., Vo, M., Higginson, S. and Kim, K. H. (1998). Ligand-dependent regulation of retinoic acid receptor alpha in rat testis: in vivo response to depletion and repletion of vitamin A. Endocrinology 139, 1239-1248. - PubMed
-
- Bjorndahl, L., Soderlund, I. and Kvist, U. (2003). Evaluation of the one-step eosin-nigrosin staining technique for human sperm vitality assessment. Hum. Reprod. 18, 813-816. - PubMed
-
- Braun, R. E., Peschon, J. J., Behringer, R. R., Brinster, R. L. and Palmiter, R. D. (1989). Protamine 3′-untranslated sequences regulate temporal translational control and subcellular localization of growth hormone in spermatids of transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 3, 793-802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

