Protective effects of resveratrol and quercetin against MPP+ -induced oxidative stress act by modulating markers of apoptotic death in dopaminergic neurons
- PMID: 19466539
- PMCID: PMC11505805
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-009-9411-5
Protective effects of resveratrol and quercetin against MPP+ -induced oxidative stress act by modulating markers of apoptotic death in dopaminergic neurons
Abstract
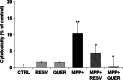
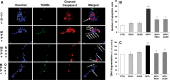
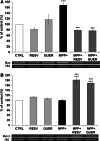
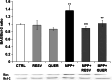
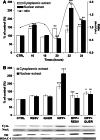
Reactive oxygen species produced by oxidative stress may participate in the apoptotic death of dopamine neurons distinctive of Parkinson's disease. Resveratrol, a red wine extract, and quercetin, found mainly in green tea, are two natural polyphenols, presenting antioxidant properties in a variety of cellular paradigms. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of resveratrol and quercetin on the apoptotic cascade induced by the administration of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP(+)), a Parkinsonian toxin, provoking the selective degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Our results show that a pre-treatment for 3 h with resveratrol or quercetin before MPP(+) administration could greatly reduce apoptotic neuronal PC12 death induced by MPP(+). We also demonstrated that resveratrol or quercetin modulates mRNA levels and protein expression of Bax, a pro-apoptotic gene, and Bcl-2, an anti-apoptotic gene. We then evaluated the release of cytochrome c and the nuclear translocation of the apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF). Altogether, our results indicate that resveratrol and quercetin diminish apoptotic neuronal cell death by acting on the expression of pro- and anti-apoptotic genes. These findings support the role of these natural polyphenols in preventive and/or complementary therapies for several human neurodegenerative diseases caused by oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Figures

References
-
- Akaneya Y, Takahashi M, Hatanaka H (1995) Involvement of free radicals in MPP+ neurotoxicity against rat dopaminergic neurons in culture. Neurosci Lett 193:53–56. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(95)11668-M - PubMed
-
- Alexaki VI, Charalampopoulos I, Kampa M, Vassalou H, Theodoropoulos P, Stathopoulos EN, Hatzoglou A, Gravanis A, Castanas E (2004) Estrogen exerts neuroprotective effects via membrane estrogen receptors and rapid Akt/NOS activation. FASEB J 18:1594–1596 - PubMed
-
- Alvira D, Yeste-Velasco M, Folch J, Verdaguer E, Canudas AM, Pallas M, Camins A (2007) Comparative analysis of the effects of resveratrol in two apoptotic models: inhibition of complex I and potassium deprivation in cerebellar neurons. Neuroscience 147:746–756. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.04.029 - PubMed
-
- Ando A, Yamazaki Y, Kaneko S, Miyake M, Nambu R, Taomoto M, Unezaki S, Okuda-Ashitaka E, Okumura T, Ito S, Matsumura M (2005) Cytoprotection by nipradilol, an anti-glaucomatous agent, via down-regulation of apoptosis related gene expression and activation of NF-kappaB. Exp Eye Res 80:501–507. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2004.10.014 - PubMed
-
- Anekonda TS (2006) Resveratrol–a boon for treating Alzheimer’s disease? Brain Res Brain Res Rev 52:316–326. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2006.04.004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

