Basement membrane proteoglycans: modulators Par Excellence of cancer growth and angiogenesis
- PMID: 19466598
- PMCID: PMC6712562
- DOI: 10.1007/s10059-009-0069-0
Basement membrane proteoglycans: modulators Par Excellence of cancer growth and angiogenesis
Abstract
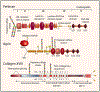
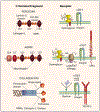
Proteoglycans located in basement membranes, the nanostructures underling epithelial and endothelial layers, are unique in several respects. They are usually large, elongated molecules with a collage of domains that share structural and functional homology with numerous extracellular matrix proteins, growth factors and surface receptors. They mainly carry heparan sulfate side chains and these contribute not only to storing and preserving the biological activity of various heparan sulfate-binding cytokines and growth factors, but also in presenting them in a more "active configuration" to their cognate receptors. Abnormal expression or deregulated function of these proteoglycans affect cancer and angiogenesis, and are critical for the evolution of the tumor microenvironment. This review will focus on the functional roles of the major heparan sulfate proteoglycans from basement membrane zones: perlecan, agrin and collagen XVIII, and on their roles in modulating cancer growth and angiogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Abdollahi A, Hahnfeldt P, Maercker C, Gröne H-J, Debus J, Ansorge W, Folkman J, Hlatky L, and Huber PE (2004). Endostatin’s antioangiogenic signaling network. Mol. Cell 13, 649–663. - PubMed
-
- Adatia R, Albini A, Carlone S, Giunciuglio D, Benelli R, Santi L, and Noonan DM (1998). Suppression of invasive behavior of melanoma cells by stable expression of anti-sense perlecan cDNA. Ann. Oncol 8, 1257–1261. - PubMed
-
- Adkins JN, Varnum SM, Auberry KJ, Moore RJ, Angell NH, Smith RD, Springer DL, and Pounds JG (2002). Toward a human blood serum proteome. Analysis by multidimensional separation coupled with mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom 1, 947–955. - PubMed
-
- Arikawa-Hirasawa E, Watanabe E, Takami H, Hassell JR, and Yamada Y (1999). Perlecan is essential for cartilage and cephalic development. Nature Genet. 23, 354–358. - PubMed
-
- Aviezer D, Hecht D, Safran M, Eisinger M, David G, and Yayon A (1994). Perlecan, basal lamina proteoglycan, promotes basic fibroblast growth factor-receptor binding, mitogenesis, and angiogenesis. Cell 79, 1005–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

