Chronic ketamine impairs fear conditioning and produces long-lasting reductions in auditory evoked potentials
- PMID: 19467327
- PMCID: PMC2726963
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.05.012
Chronic ketamine impairs fear conditioning and produces long-lasting reductions in auditory evoked potentials
Abstract
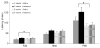
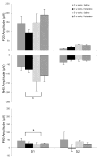
Ketamine is an NMDA receptor antagonist with a variety of uses, ranging from recreational drug to pediatric anesthetic and chronic pain reliever. Despite its value in the clinical setting, little is known about the immediate and long-lasting effects of repeated ketamine treatment. We assessed the effects of chronic administration of a subanesthetic dose of ketamine on contextual fear conditioning, detection of pitch deviants and auditory gating. After four, but not two, weeks of daily ketamine injections, mice exhibited decreased freezing in the fear conditioning paradigm. Gating of the P80 component of auditory evoked potentials was also significantly altered by treatment condition, as ketamine caused a significant decrease in S1 amplitude. Additionally, P20 latency was significantly increased as a result of ketamine treatment. Though no interactions were found involving test week, stimulus and treatment condition, these results suggest that repeated ketamine administration impairs fear memory and has lasting effects on encoding of sensory stimuli.
Figures
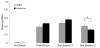

References
-
- Amann LC, Phillips JM, et al. Male and female mice differ for baseline and nicotine-induced event related potentials. Behav Neurosci. 2008;122(5):982–90. - PubMed
-
- Berman RM, Cappiello A, et al. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;47(4):351–4. - PubMed
-
- Brockhaus-Dumke A, Schultze-Lutter F, et al. Sensory gating in schizophrenia: P50 and N100 gating in antipsychotic-free subjects at risk, first-episode, and chronic patients. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;64(5):376–84. - PubMed
-
- Brown K, Gordon E, et al. Misattribution of sensory input reflected in dysfunctional target:non-target ERPs in schizophrenia. Psychol Med. 2000;30(6):1443–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

