Integrating microfluidics and lensless imaging for point-of-care testing
- PMID: 19467854
- PMCID: PMC2733855
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2009.03.037
Integrating microfluidics and lensless imaging for point-of-care testing
Abstract
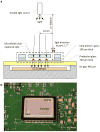
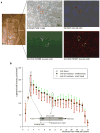
We demonstrate an integrated platform that merges a microfluidic chip with lensless imaging to target CD4(+) T-lymphocyte counts for HIV point-of-care testing at resource-limited settings. The chips were designed and fabricated simply with a laser cutter without using expensive cleanroom equipment. To capture CD4(+) T-lymphocytes from blood, anti-CD4 antibody was immobilized on only one side of the microfluidic chip. These captured cells were detected through an optically clear chip using a charge coupled device (CCD) sensor by lensless shadow imaging techniques. Gray scale image of the captured cells in a 24 mm x 4 mm x 50 microm microfluidic chip was obtained by the lensless imaging platform. The automatic cell counting software enumerated the captured cells in 3s. Captured cells were also imaged with a fluorescence microscope and manually counted to characterize functionality of the integrated platform. The integrated platform achieved 70.2+/-6.5% capture efficiency, 88.8+/-5.4% capture specificity for CD4(+) T-lymphocytes, 96+/-1.6% CCD efficiency, and 83.5+/-2.4% overall platform performance (n=9 devices) compared to the gold standard, i.e. flow cytometry count. The integrated system gives a CD4 count from blood within 10 min. The integrated platform points a promising direction for point-of-care testing (POCT) to rapidly capture, image and count subpopulations of cells from blood samples in an automated matter.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

