The RASopathies: developmental syndromes of Ras/MAPK pathway dysregulation
- PMID: 19467855
- PMCID: PMC2743116
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.04.001
The RASopathies: developmental syndromes of Ras/MAPK pathway dysregulation
Abstract
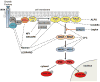
The Ras/mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is essential in the regulation of the cell cycle, differentiation, growth and cell senescence, all of which are critical to normal development. It is therefore not surprising that its dysregulation has profound effects on development. A class of developmental syndromes, the 'RASopathies', is caused by germline mutations in genes that encode protein components of the Ras/MAPK pathway. The vast majority of these mutations result in increased signal transduction down the Ras/MAPK pathway, but usually to a lesser extent than somatic mutations associated with oncogenesis. Each syndrome exhibits unique phenotypic features, however, since they all cause dysregulation of the Ras/MAPK pathway, there are numerous overlapping phenotypic features between the syndromes, including characteristic facial features, cardiac defects, cutaneous abnormalities, neurocognitive delay and a predisposition to malignancies. Here we review the clinical and underlying molecular basis for each of these syndromes.
Figures
References
-
- Bos JL. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4682–4689. - PubMed
-
- Yoon S, Seger R. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors. 2006;24:21–44. - PubMed
-
- Tartaglia M, Mehler EL, Goldberg R, Zampino G, Brunner HG, Kremer H, van der Burgt I, Crosby AH, Ion A, Jeffery S, et al. Mutations in PTPN11, encoding the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2, cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet. 2001;29:465–468. This is the first paper to identify mutations in the PTPN11 gene being responsible for approximately 50% of Noonan syndrome cases. - PubMed
-
- Schubbert S, Zenker M, Rowe SL, Boll S, Klein C, Bollag G, van der Burgt I, Musante L, Kalscheuer V, Wehner LE, et al. Germline KRAS mutations cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet. 2006;38:331–336. This is the first report of mutations in KRAS associated with a small percentage of Noonan syndrome cases. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

