Processing of thymine glycol in a clustered DNA damage site: mutagenic or cytotoxic
- PMID: 19468043
- PMCID: PMC2715253
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp422
Processing of thymine glycol in a clustered DNA damage site: mutagenic or cytotoxic
Abstract
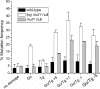
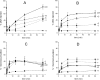
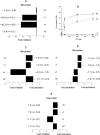
Localized clustering of damage is a hallmark of certain DNA-damaging agents, particularly ionizing radiation. The potential for genetic change arising from the effects of clustered damage sites containing combinations of AP sites, 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoG) or 5,6-dihydrothymine is high. To date clusters containing a DNA base lesion that is a strong block to replicative polymerases, have not been explored. Since thymine glycol (Tg) is non-mutagenic but a strong block to replicative polymerases, we have investigated whether clusters containing Tg are highly mutagenic or lead to potentially cytotoxic lesions, when closely opposed to either 8-oxoG or an AP site. Using a bacterial plasmid-based assay and repair assays using cell extracts or purified proteins, we have shown that DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) arise when Tg is opposite to an AP site, either through attempted base excision repair or at replication. In contrast, 8-oxoG opposite to Tg in a cluster 'protects' against DSB formation but does enhance the mutation frequency at the site of 8-oxoG relative to that at a single 8-oxoG, due to the decisive role of endonucleases in the initial stages of processing Tg/8-oxoG clusters, removing Tg to give an intermediate with an abasic site or single-strand break.
Figures


References
-
- O’Neill P, Wardman P. Radiation chemistry comes before radiation biology. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009;85:9–25. - PubMed
-
- Cadet J, Carell T, Cellia L, Chatgilialoglu C, Gimisis T, Miranda M, O’Neill P, Ravanat J-L, Robert M. DNA damage and radical reactions: mechanistic aspects, formation in cells and repair studies. Chimia. 2008;62:742–749.
-
- Ward JF. The complexity of DNA damage: relevance to biological consequences. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1994;66:427–432. - PubMed
-
- Goodhead DT. Initial events in the cellular effects of ionizing radiations: clustered damage in DNA. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1994;65:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Nikjoo H, O’Neill P, Wilson WE, Goodhead DT. Computational approach for determining the spectrum of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation. Radiat. Res. 2001;156:577–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

