Mitotic control of kinetochore-associated dynein and spindle orientation by human Spindly
- PMID: 19468067
- PMCID: PMC2711594
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200812167
Mitotic control of kinetochore-associated dynein and spindle orientation by human Spindly
Abstract
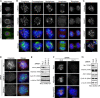
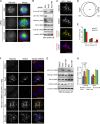
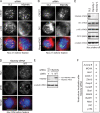
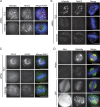
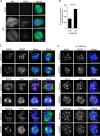
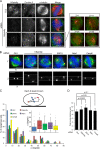
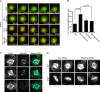
Mitotic spindle formation and chromosome segregation depend critically on kinetochore-microtubule (KT-MT) interactions. A new protein, termed Spindly in Drosophila and SPDL-1 in C. elegans, was recently shown to regulate KT localization of dynein, but depletion phenotypes revealed striking differences, suggesting evolutionarily diverse roles of mitotic dynein. By characterizing the function of Spindly in human cells, we identify specific functions for KT dynein. We show that localization of human Spindly (hSpindly) to KTs is controlled by the Rod/Zw10/Zwilch (RZZ) complex and Aurora B. hSpindly depletion results in reduced inter-KT tension, unstable KT fibers, an extensive prometaphase delay, and severe chromosome misalignment. Moreover, depletion of hSpindly induces a striking spindle rotation, which can be rescued by co-depletion of dynein. However, in contrast to Drosophila, hSpindly depletion does not abolish the removal of MAD2 and ZW10 from KTs. Collectively, our data reveal hSpindly-mediated dynein functions and highlight a critical role of KT dynein in spindle orientation.
Figures


References
-
- Basto R., Gomes R., Karess R.E. 2000. Rough deal and Zw10 are required for the metaphase checkpoint in Drosophila.Nat. Cell Biol. 2:939–943 - PubMed
-
- Basto R., Scaerou F., Mische S., Wojcik E., Lefebvre C., Gomes R., Hays T., Karess R. 2004. In vivo dynamics of the rough deal checkpoint protein during Drosophila mitosis.Curr. Biol. 14:56–61 - PubMed
-
- Buffin E., Lefebvre C., Huang J., Gagou M.E., Karess R.E. 2005. Recruitment of Mad2 to the kinetochore requires the Rod/Zw10 complex.Curr. Biol. 15:856–861 - PubMed
-
- Busson S., Dujardin D., Moreau A., Dompierre J., De Mey J.R. 1998. Dynein and dynactin are localized to astral microtubules and at cortical sites in mitotic epithelial cells.Curr. Biol. 8:541–544 - PubMed
-
- Chan G.K., Jablonski S.A., Starr D.A., Goldberg M.L., Yen T.J. 2000. Human Zw10 and ROD are mitotic checkpoint proteins that bind to kinetochores.Nat. Cell Biol. 2:944–947 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

