Pneumococcal serotypes and mortality following invasive pneumococcal disease: a population-based cohort study
- PMID: 19468297
- PMCID: PMC2680036
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000081
Pneumococcal serotypes and mortality following invasive pneumococcal disease: a population-based cohort study
Abstract
Background: Pneumococcal disease is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between specific pneumococcal serotypes and mortality from invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD).
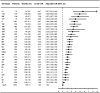
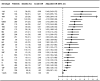
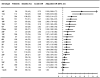
Methods and findings: In a nationwide population-based cohort study of IPD in Denmark during 1977-2007, 30-d mortality associated with pneumococcal serotypes was examined by multivariate logistic regression analysis after controlling for potential confounders. A total of 18,858 IPD patients were included. Overall 30-d mortality was 18%, and 3% in children younger than age 5 y. Age, male sex, meningitis, high comorbidity level, alcoholism, and early decade of diagnosis were significantly associated with mortality. Among individuals aged 5 y and older, serotypes 31, 11A, 35F, 17F, 3, 16F, 19F, 15B, and 10A were associated with highly increased mortality as compared with serotype 1 (all: adjusted odds ratio >or=3, p<0.001). In children younger than 5 y, associations between serotypes and mortality were different than in adults but statistical precision was limited because of low overall childhood-related mortality.
Conclusions: Specific pneumococcal serotypes strongly and independently affect IPD associated mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- [No authors listed] Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine for childhood immunization-WHO position paper. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2007;82:93–104. - PubMed
-
- Cherian T. WHO expert consultation on serotype composition of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines for use in resource-poor developing countries, 26–27 October 2006, Geneva. Vaccine. 2007;25:6557–6564. - PubMed
-
- Sinha A, Levine O, Knoll MD, Muhib F, Lieu TA. Cost-effectiveness of pneumococcal conjugate vaccination in the prevention of child mortality: an international economic analysis. Lancet. 2007;369:389–396. - PubMed
-
- Hicks LA, Harrison LH, Flannery B, Hadler JL, Schaffner W, et al. Incidence of pneumococcal disease due to non-pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV7) serotypes in the United States during the era of widespread PCV7 vaccination, 1998–2004. J Infect Dis. 2007;196:1346–1354. - PubMed
-
- Hanage WP. Serotype replacement in invasive pneumococcal disease: where do we go from here? J Infect Dis. 2007;196:1282–1284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

