Coenzyme autocatalytic network on the surface of oil microspheres as a model for the origin of life
- PMID: 19468342
- PMCID: PMC2680650
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms10041838
Coenzyme autocatalytic network on the surface of oil microspheres as a model for the origin of life
Abstract
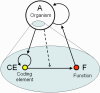
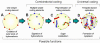
Coenzymes are often considered as remnants of primordial metabolism, but not as hereditary molecules. I suggest that coenzyme-like molecules (CLMs) performed hereditary functions before the emergence of nucleic acids. Autocatalytic CLMs modified (encoded) surface properties of hydrocarbon microspheres, to which they were anchored, and these changes enhanced autocatalysis and propagation of CLMs. Heredity started from a single kind of self-reproducing CLM, and then evolved into more complex coenzyme autocatalytic networks containing multiple kinds of CLMs. Polymerization of CLMs on the surface of microspheres and development of template-based synthesis is a potential evolutionary path towards the emergence of nucleic acids.
Keywords: Origin of life; RNA world; coding relation; coenzyme world; hydrocarbon.
Figures
References
-
- Mulkidjanian AY, Galperin MY. Physico-chemical and evolutionary constraints for the formation and selection of first biopolymers: Towards the consensus paradigm of the abiogenic origin of life. Chem. Biodivers. 2007;4:2003–2015. - PubMed
-
- Pross A. Causation and the origin of life. Metabolism or replication first? Origins Life Evol. Biosphere. 2004;34:307–321. - PubMed
-
- Copley SD, Smith E, Morowitz HJ. The origin of the RNA world: Co-evolution of genes and metabolism. Bioorg. Chem. 2007;35:430–443. - PubMed
-
- Kauffman SA. Autocatalytic sets of proteins. J. Theor. Biol. 1986;119:1–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

