Differences in the structural features of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and low-grade prostatic adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 19468392
- PMCID: PMC2684265
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-1591.40610
Differences in the structural features of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and low-grade prostatic adenocarcinoma
Abstract
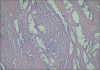
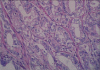
Aim: Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) is a small glandular proliferation that has histological similarities with Gleason grade 1 and 2 prostatic adenocarcinoma (PACG1,2). There are no distinct histomorphological criteria distinguishing these two lesions from each other and other small glandular proliferations. Because treatment approaches are different for these lesions, it is necessary to determine histological criteria. The aim of this study is to review the histological features of these two lesions and to define new histological criteria distinguishing AAH from PACG1,2. We, therefore, assessed 18 anatomical and structural parameters.
Materials and methods: We found 11 AAH (22 foci) and 15 PACG1,2 (22 foci) cases in 105 radical prostatectomy specimens. Basal cell-specific antikeratin was applied to these lesions. We assumed that PACG1,2 lesions did have not basal cells and we grouped the lesions as AAH and PACG1,2 based on this assumption.
Results: We found differences between AAH and PACG1,2 lesions for some parameters including the number of glands, structures such as the main ductus and basal cells. We found similar properties in the two lesions for the following parameters: localization, multiplicity, diameter of the lesion, focus asymmetry, distance between glands, inflammatory cells in and out of the lesions, secretory cell shape on the luminal side, papillary projection towards the luminal side of gland, the shape of the outer gland, the infiltrative pattern of the gland, glandular pleomorphism, biggest gland diameter and median gland diameter.
Conclusion: We determined that concurrent evaluation of histomorphological features was important to differentiate between AAH and PACG1,2.
Keywords: Adenosis; cancer; hyperplasia; low grade; proliferations; prostate; small glandular.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Nucleolar and AgNOR-analysis of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN), atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) and prostatic carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 1995 Jun;191(5):381-90. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80723-5. Pathol Res Pract. 1995. PMID: 7479355
-
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia of the prostate: morphologic criteria for its distinction from well-differentiated carcinoma.Hum Pathol. 1993 Aug;24(8):819-32. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90131-y. Hum Pathol. 1993. PMID: 8375853
-
Mucin expression in atypical adenomatous hyperplasia of the prostate.Hum Pathol. 1995 Aug;26(8):887-91. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90012-8. Hum Pathol. 1995. PMID: 7543443
-
The significance of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia for the development of prostate carcinoma. An update.Virchows Arch. 1995;426(5):425-34. doi: 10.1007/BF00193163. Virchows Arch. 1995. PMID: 7543337 Review.
-
[Benign microglandular prostate lesions. Diagnostic criteria na differential diagnosis].Pathologe. 1998 Jan;19(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s002920050249. Pathologe. 1998. PMID: 9541937 Review. German.
References
-
- Montironi R, Mazzucchelli R, Lopez-Beltran A, Cheng L, Scarpelli M. Mechanisms of disease: high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and other proposed preneoplastic lesions in the prostate. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2007;4:321–32. - PubMed
-
- Chrisofos M, Papatsoris AG, Lazaris A, Deliveliotis C. Precursor lesions of prostate cancer. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2007;44:243–70. - PubMed
-
- Anim JT, Ebrahim BH, Sathar SA. Benign disorders of the prostate: A histopathological study. Ann Saudi Med. 1998;18:22–7. - PubMed
-
- Stamatiou K, Alevizos A, Natzar M, Mihas C, Mariolis A, Michalodimitrakis E, Sofras F. Associations among benign prostate hypertrophy, atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and latent carcinoma of the prostate. Asian J Androl. 2007;9:229–33. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Beltran A, Qian J, Montironi R, Luque RJ, Bostwick DG. Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (adenosis) of the prostate: DNA ploidy analysis and immunophenotype. Int J Surg Pathol. 2005;13:167–73. - PubMed

