The penile cuff test: A clinically useful non-invasive urodynamic investigation to diagnose men with lower urinary tract symptoms
- PMID: 19468441
- PMCID: PMC2684319
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-1591.45549
The penile cuff test: A clinically useful non-invasive urodynamic investigation to diagnose men with lower urinary tract symptoms
Abstract
Objectives: To summarize the development of a novel non-invasive test to categorize voiding dysfunction in men complaining of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) - the penile cuff test.
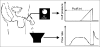
Methods: The test involves the controlled inflation of a penile cuff during micturition to interrupt voiding and hence estimate isovolumetric bladder pressure (p(ves.isv)). The validity, reliability, and clinical usefulness of the test were determined in a number of studies in men with LUTS.
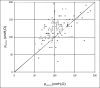
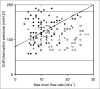
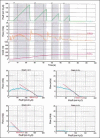
Results: The penile cuff test can be successfully performed in over 90% of men with LUTS. The reading of cuff pressure at flow interruption (p(cuff.int)) gives a valid and reliable estimate of invasively-measured p(ves.isv) and when combined with the reading for maximum flow rate obtained during the test (Q(max)) produces an accurate categorization of bladder outlet obstruction (BOO). Use of this categorization prior to treatment allows improved prediction of outcome from prostatectomy.
Conclusion: The penile cuff test fulfils the criteria as a useful clinical measurement technique applicable to the diagnosis and treatment planning of men with LUTS.
Keywords: Bladder outlet obstruction; non-invasive urodynamics; urinary symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Boyle P, Robertson C, Mazzetta C, Keech M, Hobbs FD, Fourcade R, et al. The prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms in men and women in four centres: The UrEpik study. BJU Int. 2003;92:409–14. - PubMed
-
- Homma Y. Pressure-flow studies in benign prostatic hyperplasia: To do or not to do for the patient. BJU Int. 2001;87:19–23. - PubMed
-
- Van Mastrigt R, Pel JJ. Towards a non-invasive diagnosis of bladder outlet obstruction. BJU Int. 1999;84:195–203. - PubMed
-
- Brindley G, Craggs M. The effect of atropine on the urinary bladder of the baboon and of man. J Physiol. 1975:256–55. - PubMed
-
- McRae LP, Bottaccini MR, Gleason D. Noninvasive quantitative method for measuring isovolumetric bladder pressure and urethral resistance in the male: I, Experimental validation of the theory. Neurourol Urodyn. 1995;14:101–14. - PubMed

