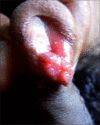
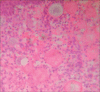
Genitourinary rhinosporidiosis
- PMID: 19468483
- PMCID: PMC2684352
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-1591.42632
Genitourinary rhinosporidiosis
Abstract
Rhinosporidiosis is a chronic granulomatous condition commonly affecting the anterior nares and nasopharynx. Apart from these two sites, infection in other sites is very rare. Here is a review of rhinosporidiosis in genitourinary organs with addition of five new cases.
Keywords: Genitourinary; rhinosporidiosis; urethra.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Karunaratne WA. Rhinosporidiosis in man. University of London: Athlone Press; 1964. pp. 14–8.
-
- Sasidharan K, Subramonian P, Moni VN, Aravindan KP, Chally R. Urethral rhinosporidiosis: Analysis of 27 cases. Br J Urol. 1985;59:66–9. - PubMed
-
- Hanchanale VS, Rao AR. A case of urethral rhinosporidiosis. Urology. 2005;66:1106–7. - PubMed
-
- Symmers WS. Deep-seated fungal infections currently seen in the histopathological service of a medical school laboratory in Britain. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966;46:514–37. - PubMed
-
- Nair S, Hannah P. Rhinosporidiosis of vagina: A case report. J Trop Med Hyg. 1987;90:329. - PubMed