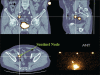
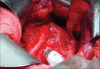
The sentinel node concept in prostate cancer: Present reality and future prospects
- PMID: 19468495
- PMCID: PMC2684382
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-1591.44246
The sentinel node concept in prostate cancer: Present reality and future prospects
Abstract
A sentinel node (SN) is defined as the first site where cancer cells are carried by lymph flow from a tumor. If this definition (SN concept) correctly reflects the clinical reality, intraoperative SN biopsy would facilitate precise nodal staging. In malignant melanoma, a prolonged survival has been evidenced by a large-scale randomized controlled study. On the contrary, research on SN concept in deeply located cancers including prostate cancer, is still investigative, and no concrete data from clinical trials are yet available. Since 1993, several investigators have demonstrated that the SN concept could be applied in prostate cancer patients as well with high accuracy. Although promising and technically feasible in pre-clinical settings, many hurdles remain to be cleared before clinical application can be recommended. This review addresses the current status and related issues of the SN concept in prostate cancer, and discusses the future directions.
Keywords: Lymph node dissection; prostatic neoplasm; sentinel node.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical applications of sentinel lymph-node biopsy for the staging and treatment of solid neoplasms.Minerva Chir. 2005 Aug;60(4):217-33. Minerva Chir. 2005. PMID: 16166921 Review. English, Italian.
-
Specification of potential indications and contraindications of sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2000;157:228-36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-57151-0_20. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10857176
-
The 'Sentinel Node' Concept: More Questions Raised than Answers Provided?Oncologist. 1998;3(5):VI-VII. Oncologist. 1998. PMID: 10388128
-
The role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with local recurrence or in-transit metastasis of melanoma.Anticancer Res. 2014 Jun;34(6):3197-203. Anticancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24922694
-
Sentinel lymph node as a new marker for therapeutic planning in breast cancer patients.J Surg Oncol. 2004 Mar;85(3):102-11. doi: 10.1002/jso.20022. J Surg Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14991881 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the TLK1-MK5 Axis Suppresses Prostate Cancer Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;17(7):1187. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071187. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227796 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo prostate cancer research: Key interspecies prostate anatomical features for translation medicine.Open Vet J. 2023 Jun;13(6):782-793. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2023.v13.i6.13. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Open Vet J. 2023. PMID: 37545707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Value of Radio-Guided Sentinel Node Detection in Patients with Prostate Cancer Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy with Modified-Extended Lymphadenectomy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 13;14(20):5012. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205012. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291796 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic sentinel lymph node (SLN) versus extensive pelvic dissection for clinically localized prostate carcinoma.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012 Feb;39(2):291-9. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-1975-x. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22086144
-
Utility of Lymphadenectomy in Prostate Cancer: Where Do We Stand?J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 22;11(9):2343. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092343. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hricak H, Choyke PL, Eberhardt SC, Leibel SA, Scardino PT. Imaging prostate cancer: A multidisciplinary perspective. Radiology. 2007;243:29–53. - PubMed
-
- Morton DL, Wen DR, Wong JH, Economou JS, Cagle LA, Storm FK, et al. Technical details of intraoperative lymphatic mapping for early stage melanoma. Arc Surg. 1992;27:392–9. - PubMed
-
- Mabry H, Giuliano AE. Sentinel node mapping for breast cancer: Progress to date and prospects for the future. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2007;16:55–70. - PubMed
-
- Morton DL, Thompson JF, Cochran AJ, Mozzillo N, Elashoff R, Essner R, et al. Sentinel-node biopsy or nodal observation in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1307–17. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda M, Egawa M, Imao T, Takashima H, Yokoyama K, Namiki M. Detection of micrometastasis by step section and immunohistochemistry in patients with prostate cancer. J Urol. 2007;177:1313–7. - PubMed