Stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes survival of pancreatic beta cells by the stabilisation of beta-catenin and activation of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2)
- PMID: 19468708
- PMCID: PMC4085163
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-009-1384-x
Stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes survival of pancreatic beta cells by the stabilisation of beta-catenin and activation of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2)
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) is a chemokine produced in stromal tissues in multiple organs. Earlier we reported on levels of SDF-1 and SDF-1 receptor (CXCR4) in the insulin-producing beta cells of the mouse pancreas and determined that the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis is important for beta cell survival through activation of the prosurvival kinase, protein kinase B (AKT). Since AKT is known to modulate the wingless-type MMTV integration site family (WNT) signalling cascade, we examined the effects of SDF-1/CXCR4 on WNT signalling in beta cells and whether this signalling is important for cell survival.
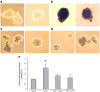
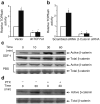
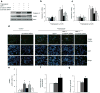
Methods: Activation of downstream WNT signalling (beta-catenin and transcription factor 7-like 2, [TCF7L2]) in response to SDF-1 was examined in the islets of WNT signalling reporter (Tcf-optimal promoter beta-galactosidase) mice and in INS-1 and MIN6 beta cells. Cytoprotection of beta cells by SDF-1 in response to the induction of apoptosis was assessed by caspase 3 and TUNEL assays.
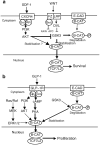
Results: SDF-1 induced WNT signalling in beta cells of isolated islets and in INS-1 cells via CXCR4-mediated activation of Galphai/o-coupled signalling and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signalling cascade resulting in the inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3-beta. The key WNT signalling regulators, beta-catenin and AKT, were activated by SDF-1 at the transcriptional and post-translational levels. Specific inhibition of beta-catenin in the WNT signalling cascade reversed the anti-apoptotic effects of SDF-1.
Conclusions/interpretation: SDF-1 promotes pancreatic beta cell survival via activation of AKT and downstream WNT signalling via the stabilisation and activation of beta-catenin/TCF7L2 transcriptional activators. These findings suggest a mechanism for SDF-1 based glucose-lowering therapies by enhancing beta cell mass through increasing cell survival.
Figures
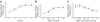
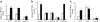
References
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52:102–110. - PubMed
-
- Yano T, Liu Z, Donovan J, Thomas MK, Habener JF. Stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1)/CXCL12 attenuates diabetes in mice and promotes pancreatic beta-cell survival by activation of the prosurvival kinase AKT. Diabetes. 2007;56:2946–2957. - PubMed
-
- Burger JA, Kipps TJ. CXCR4 a key receptor in the crosstalk between tumor cells and their microenvironment. Blood. 2006;107:1761–1767. - PubMed
-
- Kucia M, Ratajczak J, Ratajczak MZ. Bone marrow as a source of circulating CXCR4+ tissue-committed stem cells. Biol Cell. 2005;97:133–146. - PubMed
-
- Ratajczak MZ, Zuba-Surma E, Kucia M, Reca R, Wojakowski W, Ratajczak J. The pleiotropic effects of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis in organogenesis, regeneration and tumorigenesis. Leukemia. 2006;20:1915–1924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

