Dantrolene can reduce secondary damage after spinal cord injury
- PMID: 19468761
- PMCID: PMC2899378
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-009-1033-6
Dantrolene can reduce secondary damage after spinal cord injury
Abstract
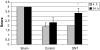
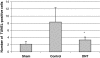
The aim of this experimental study was to investigate the possible protective effects of dantrolene on traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI). Twenty-four New Zealand rabbits were divided into three groups: Sham (no drug or operation, n = 8), Control (SCI + 1 mL saline intraperitoneally (i.p.), n = 8), and DNT (SCI + 10 mg/kg dantrolene in 1 mL, i.p., n = 8). Laminectomy was performed at T10 and balloon catheter was applied extradurally. Four and 24 h after surgery, rabbits were evaluated according to the Tarlov scoring system. Blood, cerebrospinal fluid and tissue sample from spinal cord were taken for measurements of antioxidant status or detection of apoptosis. After 4 h SCI, all animals in control or DNT-treated groups became paraparesic. Significant improvement was observed in DNT-treated group, 24 h after SCI, with respect to control. Traumatic SCI led to an increase in the lipid peroxidation and a decrease in enzymic or non-enzymic endogenous antioxidative defense systems, and increase in apoptotic cell numbers. DNT treatment prevented lipid peroxidation and augmented endogenous enzymic or non-enzymic antioxidative defense systems. Again, DNT treatment significantly decreased the apoptotic cell number induced by SCI. In conclusion, experimental results observed in this study suggest that treatment with dantrolene possess potential benefits for traumatic SCI.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Does dexmedetomidine reduce secondary damage after spinal cord injury? An experimental study.Eur Spine J. 2009 Mar;18(3):336-44. doi: 10.1007/s00586-008-0872-x. Epub 2009 Jan 8. Eur Spine J. 2009. PMID: 19130093 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of dantrolene and methylprednisolone against spinal cord injury-induced early oxidative damage in rabbit bladder: A comparative experimental study.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019 Dec;28(12):1697-1704. doi: 10.17219/acem/110326. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31851793
-
Royal jelly can diminish secondary neuronal damage after experimental spinal cord injury in rabbits.Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Jul;50(7):2554-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2012.04.018. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22538080
-
Oxidative stress in spinal cord injury and antioxidant-based intervention.Spinal Cord. 2012 Apr;50(4):264-74. doi: 10.1038/sc.2011.111. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Spinal Cord. 2012. PMID: 21987065 Review.
-
Erythropoietin in spinal cord injury.Eur Spine J. 2009 Mar;18(3):314-23. doi: 10.1007/s00586-008-0829-0. Epub 2008 Nov 22. Eur Spine J. 2009. PMID: 19030901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Omega-conotoxin MVIIA reduces neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury by inhibiting N-type voltage-dependent calcium channels on spinal dorsal horn.Front Neurosci. 2024 Feb 26;18:1366829. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1366829. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38469570 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation & apoptosis in spinal cord injury.Indian J Med Res. 2012 Mar;135(3):287-96. Indian J Med Res. 2012. PMID: 22561613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-Course Changes and Role of Autophagy in Primary Spinal Motor Neurons Subjected to Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation: Insights Into Autophagy Changes in a Cellular Model of Spinal Cord Ischemia.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Mar 20;14:38. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00038. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32265654 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and Histopathological Study of Changes in Spinal Cord Injured Rats Supplemented with Spirulina platensis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:871657. doi: 10.1155/2014/871657. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 25152764 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of neuroglobin genetically modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on spinal cord injury in rabbits.PLoS One. 2013 May 2;8(5):e63444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063444. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ates O, Cayli SR, Altinoz E, Gurses I, Yucel N, Kocak A, Yologlu S, Turkoz Y. Effects of resveratrol and methylprednisolone on biochemical, neurobehavioral and histopathological recovery after experimental spinal cord injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006;27:1317–1325. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00416.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

