Ultrasonic characterization of ultrasound contrast agents
- PMID: 19468770
- PMCID: PMC2727586
- DOI: 10.1007/s11517-009-0497-1
Ultrasonic characterization of ultrasound contrast agents
Abstract
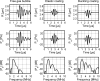
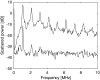
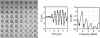
The main constituent of an ultrasound contrast agent (UCA) is gas-filled microbubbles. An average UCA contains billions per ml. These microbubbles are excellent ultrasound scatterers due to their high compressibility. In an ultrasound field they act as resonant systems, resulting in harmonic energy in the backscattered ultrasound signal, such as energy at the subharmonic, ultraharmonic and higher harmonic frequencies. This harmonic energy is exploited for contrast enhanced imaging to discriminate the contrast agent from surrounding tissue. The amount of harmonic energy that the contrast agent bubbles generate depends on the bubble characteristics in combination with the ultrasound field applied. This paper summarizes different strategies to characterize the UCAs. These strategies can be divided into acoustic and optical methods, which focus on the linear or nonlinear responses of the contrast agent bubbles. In addition, the characteristics of individual bubbles can be determined or the bubbles can be examined when they are part of a population. Recently, especially optical methods have proven their value to study individual bubbles. This paper concludes by showing some examples of optically observed typical behavior of contrast bubbles in ultrasound fields.
Figures


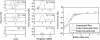


References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00004424-199505000-00008', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00004424-199505000-00008'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7558737', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7558737/'}]}
- van Liew HD, Burkard ME (1995) Behavior of bubbles of slowly permeating gas used for ultrasonic imaging contrast. Invest Radiol 30:315–321. doi:10.1097/00004424-199505000-00008 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1063/1.1747520', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1747520'}]}
- Epstein PS, Plesset MS (1950) On the stability of gas bubbles in liquid-gas solutions. J Chem Phys 18:1505–1509. doi:10.1063/1.1747520
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0301-5629(98)00034-9', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-5629(98)00034-9'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9695277', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9695277/'}]}
- Kabalnov A, Klein D, Pelura T, Schutt E, Weers J (1998) Dissolution of multicomponent microbubbles in the bloodstream: 1. Theory. Ultrasound Med Biol 24:739–749. doi:10.1016/S0301-5629(98)00034-9 - PubMed
-
- Medwin H (1977) Counting bubbles acoustically: A review. Ultrasonics 15:7–13. doi:10.1016/0041-624X(77)90005-1
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1046/j.1540-8175.2002.00229.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1540-8175.2002.00229.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12022933', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12022933/'}]}
- de Jong N, Bouakaz A, Frinking P (2002) Basic acoustic properties of microbubbles. Echocardiography 19:229–240. doi:10.1046/j.1540-8175.2002.00229.x - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

