Complications and pitfalls of lumbar interlaminar and transforaminal epidural injections
- PMID: 19468908
- PMCID: PMC2682416
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-008-9035-2
Complications and pitfalls of lumbar interlaminar and transforaminal epidural injections
Abstract
Lumbar interlaminar and transforaminal epidural injections are used in the treatment of lumbar radicular pain and other lumbar spinal pain syndromes. Complications from these procedures arise from needle placement and the administration of medication. Potential risks include infection, hematoma, intravascular injection of medication, direct nerve trauma, subdural injection of medication, air embolism, disc entry, urinary retention, radiation exposure, and hypersensitivity reactions. The objective of this article is to review the complications of lumbar interlaminar and transforaminal epidural injections and discuss the potential pitfalls related to these procedures. We performed a comprehensive literature review through a Medline search for relevant case reports, clinical trials, and review articles. Complications from lumbar epidural injections are extremely rare. Most if not all complications can be avoided by careful technique with accurate needle placement, sterile precautions, and a thorough understanding of the relevant anatomy and contrast patterns on fluoroscopic imaging.
Figures

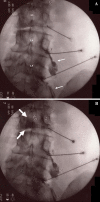
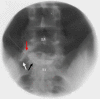
Similar articles
-
Anatomical complications of epidural anesthesia: A comprehensive review.Clin Anat. 2017 Apr;30(3):342-346. doi: 10.1002/ca.22831. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Clin Anat. 2017. PMID: 28165638 Review.
-
A prospective evaluation of complications of 10,000 fluoroscopically directed epidural injections.Pain Physician. 2012 Mar-Apr;15(2):131-40. Pain Physician. 2012. PMID: 22430650 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of epidural steroids in the management of chronic spinal pain: a systematic review of effectiveness and complications.Pain Physician. 2005 Jan;8(1):127-43. Pain Physician. 2005. PMID: 16850050
-
Interlaminar versus transforaminal epidural injections for the treatment of symptomatic lumbar intervertebral disc herniations.Pain Physician. 2006 Oct;9(4):361-6. Pain Physician. 2006. PMID: 17066121
-
Fluoroscopically Guided Epidural Injections of the Cervical and Lumbar Spine.Radiographics. 2017 Mar-Apr;37(2):537-561. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017160043. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Radiographics. 2017. PMID: 27935769 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound versus fluoroscopy-guided caudal epidural steroid injection for the treatment of chronic low back pain with radiculopathy: A randomised, controlled clinical trial.Indian J Anaesth. 2016 Jun;60(6):388-92. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.183391. Indian J Anaesth. 2016. PMID: 27330199 Free PMC article.
-
The risks of epidural and transforaminal steroid injections in the Spine: Commentary and a comprehensive review of the literature.Surg Neurol Int. 2013 Mar 22;4(Suppl 2):S74-93. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.109446. Print 2013. Surg Neurol Int. 2013. PMID: 23646278 Free PMC article.
-
Complications of injections in conservative treatment of degenerative spine disease: a prospective unicentric study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Nov 22;23(1):1002. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05970-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 36419001 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound- versus fluoroscopy-guided injections in the lower back for the management of pain: a systematic review.Eur Radiol. 2019 Jul;29(7):3401-3409. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06065-3. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30887198
-
Reducing Radiation Exposure in Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections with Pulsed Fluoroscopy: A Randomized, Double-blind, Controlled Clinical Trial.Pain Physician. 2018 Jan;21(1):53-60. Pain Physician. 2018. PMID: 29357331 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Boswell MV, Trescott AM, Datta S, American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians et al. Interventional techniques: evidence-based practice guidelines in the management of chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2007;10:7–111. - PubMed
-
- Riew KD, Yin Y, Gilula L, et al. The effect of nerve-root injections on the need for operative treatment of lumbar radicular pain. A prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blind study. J Bone Joint Am. 2000;82A:1589–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

