Long-lived Indy and calorie restriction interact to extend life span
- PMID: 19470468
- PMCID: PMC2685744
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0904115106
Long-lived Indy and calorie restriction interact to extend life span
Abstract
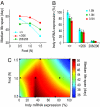
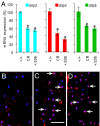
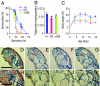
Calorie restriction (CR) improves health and extends life span in a variety of species. Despite many downstream molecules and physiological systems having been identified as being regulated by CR, the mechanism by which CR extends life span remains unclear. The Drosophila gene Indy (for I'm not dead yet), involved in the transport and storage of Krebs cycle intermediates in tissues important in fly metabolism, was proposed to regulate life span via an effect on metabolism that could overlap with CR. In this study, we report that CR down regulates Indy mRNA expression, and that CR and the level of Indy expression interact to affect longevity. Optimal life span extension is seen when Indy expression is decreased between 25 and 75% of normal. Indy long-lived flies show several phenotypes that are shared by long-lived CR flies, including decreased insulin-like signaling, lipid storage, weight gain, and resistance to starvation as well as an increase in spontaneous physical activity. We conclude that Indy and CR interact to affect longevity and that a decrease in Indy may induce a CR-like status that confers life span extension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kenyon C. The plasticity of aging: Insights from long-lived mutants. Cell. 2005;120:449–460. - PubMed
-
- Guarente L, Picard F. Calorie restriction– the SIR2 connection. Cell. 2005;120:473–482. - PubMed
-
- Lin S-J, Defossez P-A, Guarente L. Requirement of NAD and SIR2 for life-span extension by calorie restriction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 2000;289:2126–2128. - PubMed
-
- Wood JG, et al. Sirtuin activators mimic caloric restriction and delay ageing in metazoans. Nature. 2004;430:686–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG023088/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG24353/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025277/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007601/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K25 AG028753/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG024353/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG16667/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG25277/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016667/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG016667/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K25AG028753/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG23088/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG024353/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

