Overexpression of lecithin:retinol acyltransferase in the epithelial basal layer makes mice more sensitive to oral cavity carcinogenesis induced by a carcinogen
- PMID: 19471114
- PMCID: PMC2882701
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.8.13.8630
Overexpression of lecithin:retinol acyltransferase in the epithelial basal layer makes mice more sensitive to oral cavity carcinogenesis induced by a carcinogen
Abstract
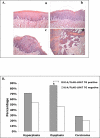
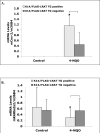
Lecithin:retinol acyltransferase (LRAT) is an enzyme that converts retinol (vitamin A) to retinyl esters. Its expression is often reduced in human cancers, including oral cavity cancers. We investigated the effects of ectopic expression of human lecithin:retinol acyltransferase (LRAT) on murine oral cavity carcinogenesis induced by the carcinogen 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4-NQO). We targeted human LRAT expression specifically to the basal layer of mouse skin and oral cavity epithelia by using a portion of the human cytokeratin 14 (K14) promoter. High levels of human LRAT transgene transcripts were detected in the tongues and skin of adult transgenic positive (TG+) mice, but not in transgenic negative (TG-) mice. The retinyl ester levels in skin of LRAT TG+ mice were 32% +/- 5.4% greater than those in TG- mice, and topical treatment of the back skin with retinol resulted in greater increases in retinyl esters (from 6.9- to 14.3-fold in different TG+ mice) in TG+ mouse skin than in TG- mouse skin (1.3 fold). While carcinogen (4-NQO) treatment induced multifocal precancerous and cancer lesions in the tongues of both TG positive (n=16) and negative mice (n=22), higher percentages of transgenic positive mice (62.5%) developed more severe tongue lesions (grades 3 and 4) than transgenic negative mice (24.8%) after 4-NQO treatment (p < 0.05). Carcinogen treatment also resulted in greater percentages of transgenic positive mouse tongues with hyperplasia (71.4%), dysplasia (85.7%, p < 0.05), and carcinoma (28.6%) than transgenic negative mouse tongues (53.3%, 46.7%, and 20%, respectively). Moreover, we observed higher cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2) and lower RARbeta(2) mRNA levels in TG+ mouse tongues as compared to TG- mouse tongues after 4-NQO treatment (p < 0.05). Taken together, these data show that overexpression of human LRAT specifically in oral basal epithelial cells makes these cells more sensitive to carcinogen induced tumorigenesis.
Figures









Comment in
-
Lecithin:retinol acyltransferase and retinyl esters: is balance the essence in carcinogenesis?Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Jul;8(13):1226-7. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.13.8902. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19483469 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Lecithin:retinol acyltransferase and retinyl esters: is balance the essence in carcinogenesis?Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Jul;8(13):1226-7. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.13.8902. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19483469 No abstract available.
-
Oral carcinogenesis induced by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide in lecithin:retinol acyltransferase gene knockout mice.J Nutr Biochem. 2010 Oct;21(10):975-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.07.012. Epub 2009 Dec 1. J Nutr Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19954945 Free PMC article.
-
Oral cavity and esophageal carcinogenesis modeled in carcinogen-treated mice.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jan 1;10(1 Pt 1):301-13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-0999-3. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 14734483
-
A DNA methyltransferase inhibitor and all-trans retinoic acid reduce oral cavity carcinogenesis induced by the carcinogen 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009 Dec;2(12):1100-10. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0136. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009. PMID: 19952362 Free PMC article.
-
Lecithin:Retinol Acyltransferase: A Key Enzyme Involved in the Retinoid (visual) Cycle.Biochemistry. 2016 Jun 7;55(22):3082-91. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00319. Epub 2016 May 23. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27183166 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related liver tumorigenesis is suppressed in mice lacking hepatic retinoid storage.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 7;8(41):70695-70706. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19978. eCollection 2017 Sep 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29050312 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of bexarotene and the retinoid CD1530 reduces murine oral-cavity carcinogenesis induced by the carcinogen 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 17;111(24):8907-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404828111. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24927566 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Metabonomic Investigations of Schistosoma japonicum From SCID Mice and BALB/c Mice: Clues to Developmental Abnormality of Schistosome in the Immunodeficient Host.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 12;10:440. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00440. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30915055 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular features of tongue epithelium treated with the carcinogen 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide and alcohol as a model for HNSCC.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Nov;34(11):2673-81. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt223. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23784083 Free PMC article.
-
Diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis is suppressed in lecithin:retinol acyltransferase-deficient mice primarily through retinoid actions immediately after carcinogen administration.Carcinogenesis. 2012 Feb;33(2):268-74. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr275. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22116467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amornphimoltham P, Sriuranpong V, Patel V, Benavides F, Conti CJ, Sauk J, Sausville EA, Molinolo AA, Gutkind JS. Persistent activation of the Akt pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a potential target for UCN-01. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:4029–37. - PubMed
-
- Arnold I, Watt FM. c-Myc activation in transgenic mouse epidermis results in mobilization of stem cells and differentiation of their progeny. Curr Biol. 2001;11:558–568. - PubMed
-
- Binnie WH, Rankin KV, Mackenzie IC. Etiology of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol. 1983;12:11–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
