Nonischemic cerebral venous hypertension promotes a pro-angiogenic stage through HIF-1 downstream genes and leukocyte-derived MMP-9
- PMID: 19471278
- PMCID: PMC2745831
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.67
Nonischemic cerebral venous hypertension promotes a pro-angiogenic stage through HIF-1 downstream genes and leukocyte-derived MMP-9
Abstract
Cerebral venous hypertension (VH) and angiogenesis are implicated in the pathogenesis of brain arteriovenous malformation and dural arteriovenous fistulae. We studied the association of VH and angiogenesis using a mouse brain VH model. Sixty mice underwent external jugular vein and common carotid artery (CCA) anastomosis (VH model), CCA ligation, or sham dissection (n=20). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and stromal-cell-derived factor-1alpha (SDF-1alpha) expression, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity were analyzed. We found VH animals had higher (P<0.05) sagittal sinus pressure (8+/-1 mm Hg) than control groups (1+/-1 mm Hg). Surface cerebral blood flow and mean arterial pressure did not change. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, VEGF, and SDF-1alpha expression increased (P<0.05). Neutrophils and MMP-9 activity increased 10-fold 1 day after surgery, gradually decreased afterward, and returned to baseline 2 weeks after surgery. Macrophages began to increase 3 days after surgery (P<0.05), which coincided with the changes in SDF-1alpha expression. Capillary density in the parasagittal cortex increased 17% compared with the controls. Our findings suggest that mild nonischemic VH results in a pro-angiogenic stage in the brain by upregulating HIF-1 and its downstream targets, VEGF and SDF-1alpha, increasing leukocyte infiltration and MMP-9 activity.
Figures


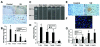
Similar articles
-
Expression of angiogenic and vasculogenic factors in human lymphedematous tissue.Lymphat Res Biol. 2011;9(3):143-9. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2011.0008. Lymphat Res Biol. 2011. PMID: 22066744
-
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in response to venous hypertension.Neurosurgery. 2006 Sep;59(3):687-96; discussion 687-96. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000228962.68204.CF. Neurosurgery. 2006. PMID: 16955051
-
Increased expression of HIF-1alpha, VEGF-A and its receptors, MMP-2, TIMP-1, and ADAMTS-1 at the venous stenosis of arteriovenous fistula in a mouse model with renal insufficiency.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010 Aug;21(8):1255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2010.02.043. Epub 2010 Jul 3. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20598569 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Overexpression of Metallothionein Prevents Diabetes-Induced Impairment in Ischemia Angiogenesis Through Preservation of HIF-1α/SDF-1/VEGF Signaling in Endothelial Progenitor Cells.Diabetes. 2020 Aug;69(8):1779-1792. doi: 10.2337/db19-0829. Epub 2020 May 13. Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32404351 Free PMC article.
-
Rnd3/RhoE Modulates Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling by Stabilizing Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α and Regulates Responsive Cardiac Angiogenesis.Hypertension. 2016 Mar;67(3):597-605. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06412. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 26781283 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Normal perfusion pressure breakthrough phenomenon: experimental models.Neurosurg Rev. 2014 Oct;37(4):559-67. doi: 10.1007/s10143-014-0549-3. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Neurosurg Rev. 2014. PMID: 24777643 Review.
-
Increased Inflammatory Response in Old Mice is Associated with More Severe Neuronal Injury at the Acute Stage of Ischemic Stroke.Aging Dis. 2019 Feb 1;10(1):12-22. doi: 10.14336/AD.2018.0205. eCollection 2019 Feb. Aging Dis. 2019. PMID: 30705764 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for hemorrhage of brain arteriovenous malformation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Oct;25(10):1085-1095. doi: 10.1111/cns.13200. Epub 2019 Jul 29. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 31359618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-culture of human fibroblasts, smooth muscle and endothelial cells promotes osteopontin induction in hypoxia.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Mar;24(5):2931-2941. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14905. Epub 2020 Feb 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32032472 Free PMC article.
-
Potential contribution of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, aquaporin-4, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 to blood-brain barrier disruption and brain edema after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage.J Mol Neurosci. 2012 Sep;48(1):273-80. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9769-6. Epub 2012 Apr 22. J Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22528459
References
-
- Aghi M, Cohen KS, Klein RJ, Scadden DT, Chiocca EA. Tumor stromal-derived factor-1 recruits vascular progenitors to mitotic neovasculature, where microenvironment influences their differentiated phenotypes. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9054–64. - PubMed
-
- Bederson JB, Wiestler OD, Brustle O, Roth P, Frick R, Yasargil MG. Intracranial venous hypertension and the effects of venous outflow obstruction in a rat model of arteriovenous fistula. Neurosurgery. 1991;29:341–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

