In vitro stimulation of HDL anti-inflammatory activity and inhibition of LDL pro-inflammatory activity in the plasma of patients with end-stage renal disease by an apoA-1 mimetic peptide
- PMID: 19471321
- PMCID: PMC3280585
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2009.177
In vitro stimulation of HDL anti-inflammatory activity and inhibition of LDL pro-inflammatory activity in the plasma of patients with end-stage renal disease by an apoA-1 mimetic peptide
Abstract
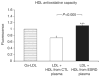
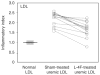
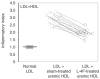
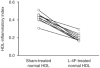
Features of end-stage renal disease such as oxidative stress, inflammation, hypertension, and dyslipidemia are associated with accelerated atherosclerosis and increased risk of death from cardiovascular disease. By inhibiting the formation and increasing the disposal of oxidized lipids, HDL exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions. Given that apolipoproteinA-1 can limit atherosclerosis, we hypothesized that an apolipoproteinA-1 mimetic peptide, 4F, may reduce the proinflammatory properties of LDL and enhance the anti-inflammatory properties of HDL in uremic plasma. To test this, plasma from each of 12 stable hemodialysis patients and age-matched control subjects was incubated with 4F or vehicle. The isolated HDL and LDL fractions were added to cultured human aortic endothelial cells to quantify monocyte chemotactic activity, thus measuring their pro- or anti-inflammatory index. The LDL from the hemodialysis patients was more pro-inflammatory and their HDL was less anti-inflammatory than those of the control subjects. Pre-incubation of the plasma from the hemodialysis patients with 4F decreased LDL pro-inflammatory activity and enhanced HDL anti-inflammatory activity. Whether 4F or other apolipoproteinA-1 mimetic peptides will have any therapeutic benefit in end-stage renal disease will have to be examined directly in clinical studies.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE
Drs Alan M Fogelman and Mohamad Navab are principals and shareholders in Bruins Pharma. The other authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Comment in
-
Potential restoration of HDL function with apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide in end-stage renal disease.Kidney Int. 2009 Aug;76(4):359-61. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.205. Kidney Int. 2009. PMID: 19644477 Review.
References
-
- Excerpts from the United States Renal Data system 2005 Annual Data Report. Atlas of end-stage renal disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47:S1–S286. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Kovesdy CP, Trivedi BK, Anderson JE. Associations of kidney function with mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease not yet on dialysis: a historical prospective cohort study. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2006;13:183–188. - PubMed
-
- Muntner P, He J, Astor BC, et al. Traditional and nontraditional risk factors predict coronary heart disease in chronic kidney disease: results from the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:529–538. - PubMed
-
- Vaziri ND. Effect of chronic renal failure on nitric oxide metabolism. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;38:S74–S79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

