Shaken baby syndrome: a common variant of non-accidental head injury in infants
- PMID: 19471629
- PMCID: PMC2680569
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2009.0211
Shaken baby syndrome: a common variant of non-accidental head injury in infants
Abstract
Background: Recent cases of child abuse reported in the media have underlined the importance of unambiguous diagnosis and appropriate action. Failure to recognize abuse may have severe consequences. Abuse of infants often leaves few external signs of injury and therefore merits special diligence, especially in the case of non-accidental head injury, which has high morbidity and mortality.
Methods: Selective literature review including an overview over national and international recommendations.
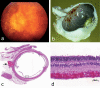
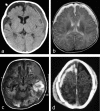
Results: Shaken baby syndrome is a common manifestation of non-accidental head injury in infancy. In Germany, there are an estimated 100 to 200 cases annually. The characteristic findings are diffuse encephalopathy and subdural and retinal hemorrhage in the absence of an adequate explanation. The mortality can be as high as 30%, and up to 70% of survivors suffer long-term impairment. Assessment of suspected child abuse requires meticulous documentation in order to preserve evidence as well as radiological, ophthalmological, laboratory, and forensic investigations.
Conclusions: The correct diagnosis of shaken baby syndrome requires understanding of the underlying pathophysiology. Assessment of suspected child abuse necessitates painstaking clinical examination with careful documentation of the findings. A multidisciplinary approach is indicated. Continuation, expansion, and evaluation of existing preventive measures in Germany is required.
Keywords: brain damage; child abuse; forensic medicine; head injury; pediatric care.
Figures
Comment in
-
Early warning signs.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2009 Jul;106(27):468; author reply 468. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2009.0468a. Epub 2009 Jul 3. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2009. PMID: 19652770 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tenney-Soeiro R, Wilson C. An update on child abuse and neglect. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2004;16:233–237. - PubMed
-
- Minns RA, Brown JK, Minns RA, Brown JK. Clinics in Developmental Medicine. London: Mac Keith Press; 2005. Neurological perspectives of non-accidental head injury and whiplash/shaken baby syndrome: An overview. Shaking and other non-accidental head injuries in children; pp. 1–106.
-
- Duhaime AC, Christian CW, Rorke LB, Zimmerman RA. Nonaccidental head injury in infants-the „shaken-baby syndrome“. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1822–1829. - PubMed
-
- Herrmann B. Nicht akzidentelle Kopfverletzungen und Schütteltrauma. Klinische und pathophysiologische Aspekte. Rechtsmedizin. 2008;18:9–16.
-
- Shaken baby syndrome: rotational cranial injuries-technical report. Pe-diatrics. 2001;108:206–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources