Amelioration of enteric neuropathology in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick C by Npc1 expression in enteric glia
- PMID: 19472223
- PMCID: PMC2853225
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.22126
Amelioration of enteric neuropathology in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick C by Npc1 expression in enteric glia
Abstract
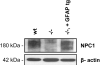
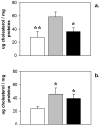
Niemann-Pick C (NPC) disease is an autosomal recessive, lethal, neurodegenerative disorder caused by mutations in NPC1. By using the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) promoter, we demonstrated previously that astrocyte-specific expression of Npc1 decreased neuronal storage of cholesterol in Npc1(-/-) mice; reduced numbers of axonal spheroids; and produced less degeneration of neurons, reactive astrocytes, and loss of myelin tracts in the central nervous system. GFAP-Npc1, Npc1(-/-) mice exhibited markedly enhanced survival, and death was not associated with the severe terminal weight loss observed in Npc1(-/-) mice. Intestinal transit is delayed in Npc1(-/-) mice but is normal in GFAP-NPC1, Npc1(-/-) until late in the course of their disease. Because glia play an important role in the enteric nervous system, we studied morphology and cholesterol content of intestines from Npc1(-/-) mice and examined the effect of GFAP-promoted restoration of Npc1 in enteric glia. Although the number of neurons was not altered, the total amount of cholesterol stored in the small intestine was decreased, as were the number of neurons with inclusions and the number of inclusions per neuron. We conclude that expression of Npc1 by enteric glial cells can ameliorate the enteric neuropathology, and we speculate that dysfunction of the enteric nervous system contributes to the retarded intestinal transit, weight loss, and demise of Npc1(-/-) mice.
2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Astrocyte-only Npc1 reduces neuronal cholesterol and triples life span of Npc1-/- mice.J Neurosci Res. 2008 Oct;86(13):2848-56. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21730. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18500759 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomically defined neuron-based rescue of neurodegenerative Niemann-Pick type C disorder.J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 23;31(12):4367-78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5981-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21430138 Free PMC article.
-
Normalization of cholesterol homeostasis by 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in neurons and glia from Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1)-deficient mice.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 16;287(12):9290-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.326405. Epub 2012 Jan 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22277650 Free PMC article.
-
In Niemann-Pick C1 mouse models, glial-only expression of the normal gene extends survival much further than do changes in genetic background or treatment with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin.Gene. 2018 Feb 15;643:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.12.006. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29223359
-
Endo-lysosomal dysfunction and neuronal-glial crosstalk in Niemann-Pick type C disease.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Apr 8;379(1899):20220388. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0388. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38368932 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current Challenges in Understanding the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C1.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 6;20(18):4392. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184392. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31500175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment trials in Niemann-Pick type C disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Dec;36(8):2215-2221. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00842-0. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 34596813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrointestinal Tract Pathology in a BALB/c Niemann-Pick Disease Type C1 Null Mouse Model.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Apr;63(4):870-880. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-4914-x. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29357083 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary function and pathology in hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextin-treated and untreated Npc1⁻/⁻ mice.Mol Genet Metab. 2011 Jun;103(2):142-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Mar 5. Mol Genet Metab. 2011. PMID: 21459030 Free PMC article.
-
Gene therapy ameliorates bowel dysmotility and enteric neuron degeneration and extends survival in lysosomal storage disorder mouse models.Sci Transl Med. 2025 Jan 15;17(781):eadj1445. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adj1445. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Sci Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39813314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borchelt DR, Davis J, Fischer M, Lee MK, Slunt HH, Ratovitsky T, Regard J, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Sisodia SS, Price DL. A vector for expressing foreign genes in the brains and hearts of transgenic mice. Genet Anal. 1996;13:159–163. - PubMed
-
- Bush TG, Savidge TC, Freeman TC, Cox HJ, Campbell EA, Mucke L, Johnson MH, Sofroniew MV. Fulminant jejuno-ileitis following ablation of enteric glia in adult transgenic mice. Cell. 1998;93:189–201. - PubMed
-
- Dinari G, Rosenbach Y, Grunebaum M, Zahavi I, Alpert G, Nitzan M. Gastrointestinal manifestations of Niemann-Pick disease. Enzyme. 1980;25:407–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

