WNT signaling enhances breast cancer cell motility and blockade of the WNT pathway by sFRP1 suppresses MDA-MB-231 xenograft growth
- PMID: 19473496
- PMCID: PMC2716500
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2317
WNT signaling enhances breast cancer cell motility and blockade of the WNT pathway by sFRP1 suppresses MDA-MB-231 xenograft growth
Abstract
Introduction: In breast cancer, deregulation of the WNT signaling pathway occurs by autocrine mechanisms. WNT ligands and Frizzled receptors are coexpressed in primary breast tumors and cancer cell lines. Moreover, many breast tumors show hypermethylation of the secreted Frizzled-related protein 1 (sFRP1) promoter region, causing low expression of this WNT antagonist. We have previously shown that the WNT pathway influences proliferation of breast cancer cell lines via activation of canonical signaling and epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation, and that interference with WNT signaling reduces proliferation. Here we examine the role of WNT signaling in breast tumor cell migration and on xenograft outgrowth.
Methods: The breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 was used to study WNT signaling. We examined the effects of activating or blocking the WNT pathway on cell motility by treatment with WNT ligands or by ectopic sFPR1 expression, respectively. The ability of sFRP1-expressing MDA-MB-231 cells to grow as xenografts was also tested. Microarray analyses were carried out to identify targets with roles in MDA-MB-231/sFRP1 tumor growth inhibition.
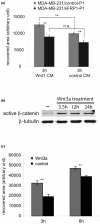
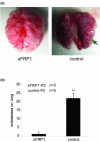
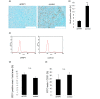
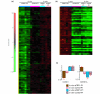
Results: We show that WNT stimulates the migratory ability of MDA-MB-231 cells. Furthermore, ectopic expression of sFRP1 in MDA-MB-231 cells blocks canonical WNT signaling and decreases their migratory potential. Moreover, the ability of MDA-MB-231/sFRP1-expressing cells to grow as xenografts in mammary glands and to form lung metastases is dramatically impaired. Microarray analyses led to the identification of two genes, CCND1 and CDKN1A, whose expression level is selectively altered in vivo in sFRP1-expressing tumors. The encoded proteins cyclin D1 and p21Cip1 were downregulated and upregulated, respectively, in sFRP1-expressing tumors, suggesting that they are downstream mediators of WNT signaling.
Conclusions: Our results show that the WNT pathway influences multiple biological properties of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. WNT stimulates tumor cell motility; conversely sFRP1-mediated WNT pathway blockade reduces motility. Moreover, ectopic sFRP1 expression in MDA-MB-231 cells has a strong negative impact on tumor outgrowth and blocked lung metastases. These results suggest that interference with WNT signaling using sFRP1 to block the ligand- receptor interaction may be a valid therapeutic approach in breast cancer.
Figures


Comment in
-
Is there more to Wnt signalling in breast cancer than stabilisation of beta-catenin?Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(4):105. doi: 10.1186/bcr2336. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19664193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howe LR, Brown AM. Wnt signaling and breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004;3:36–41. - PubMed
-
- Huguet EL, McMahon JA, McMahon AP, Bicknell R, Harris AL. Differential expression of human Wnt genes 2, 3, 4, and 7B in human breast cell lines and normal and disease states of human breast tissue. Cancer Res. 1994;54:2615–2621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

