Maxillofacial trauma patient: coping with the difficult airway
- PMID: 19473497
- PMCID: PMC2693512
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-7922-4-21
Maxillofacial trauma patient: coping with the difficult airway
Abstract
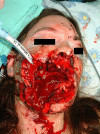
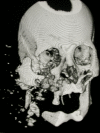
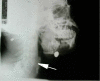
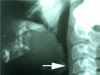
Establishing a secure airway in a trauma patient is one of the primary essentials of treatment. Any flaw in airway management may lead to grave morbidity and mortality. Maxillofacial trauma presents a complex problem with regard to the patient's airway. By definition, the injury compromises the patient's airway and it is, therefore, must be protected. In most cases, the patient undergoes surgery for maxillofacial trauma or for other, more severe, life-threatening injuries, and securing the airway is the first step in the introduction of general anaesthesia. In such patients, we anticipate difficult endotracheal intubation and, often, also difficult mask ventilation. In addition, the patient is usually regarded as having a "full stomach" and has not been cleared of a C-spine injury, which may complicate airway management furthermore. The time available to accomplish the task is short and the patient's condition may deteriorate rapidly. Both decision-making and performance are impaired in such circumstances. In this review, we discuss the complexity of the situation and present a treatment approach.
Figures
References
-
- American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma . Advanced Trauma Life Support for Doctors ATLS. 7. Chicago, IL; American College of Surgeons; 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

