Cdc42 and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway are essential for PspC-mediated internalization of pneumococci by respiratory epithelial cells
- PMID: 19473971
- PMCID: PMC2740568
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.003442
Cdc42 and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway are essential for PspC-mediated internalization of pneumococci by respiratory epithelial cells
Abstract
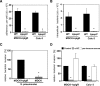
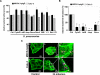
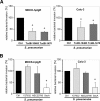
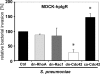
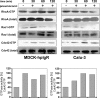
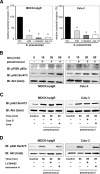
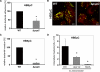
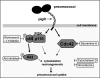
The pneumococcal surface protein C (PspC) is a major adhesin of Streptococcus pneumoniae, the cause of lobar pneumonia and invasive diseases. PspC interacts in a human-specific manner with the ectodomain of the human polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) produced by respiratory epithelial cells. By adopting the retrograde machinery of human pIgR, this protein-protein interaction promotes colonization and transcytosis across the epithelial layer. Here, we explored the role of Rho family guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (Akt) for ingestion of pneumococci via the human pIgR. Inhibition experiments suggested that the host-cell actin microfilaments and microtubules are essential for this pneumococcal uptake mechanism. By using specific GTPase-modifying toxins, inhibitors, and GTPase expression constructs we demonstrate that Cdc42, but not Rac1 and RhoA are involved in PspC-mediated invasion of pneumococci into host cells. Accordingly, Cdc42 is time-dependently activated during ingestion of pneumococci. In addition, PI3K and Akt are essential for ingestion of pneumococci by respiratory epithelial cells via the PspC-pIgR interaction. The subunit p85alpha of PI3K and Akt was activated during the infection process. Moreover, Akt activation upon pneumococcal invasion depends on PI3K. In conclusion, our results illustrate for the first time key signaling molecules of host cells that are required for PspC-pIgR-mediated invasion of pneumococci into epithelial cells. This unique and specific bacterial entry process is dependent on the cooperation and activation of Rho family GTPase Cdc42, PI3K, and Akt.
Figures
References
-
- Cartwright K. (2002) Eur. J. Pediatr. 161, 188–195 - PubMed
-
- Hammerschmidt S., Agarwal V., Kunert A., Haelbich S., Skerka C., Zipfel P. F. (2007) J. Immunol. 178, 5848–5858 - PubMed
-
- Rennemeier C., Hammerschmidt S., Niemann S., Inamura S., Zähringer U., Kehrel B. E. (2007) FASEB J. 21, 3118–3132 - PubMed
-
- Bergmann S., Lang A., Rohde M., Agarwal V., Rennemeier C., Grashoff C., Preissner K. T., Hammerschmidt S. (2009) J. Cell Sci. 122, 256–267 - PubMed
-
- Hammerschmidt S. (2006) Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9, 12–20 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

