Free thiol group of MD-2 as the target for inhibition of the lipopolysaccharide-induced cell activation
- PMID: 19473973
- PMCID: PMC2740575
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.003756
Free thiol group of MD-2 as the target for inhibition of the lipopolysaccharide-induced cell activation
Abstract
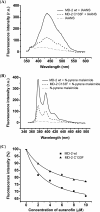
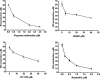
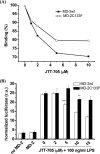
MD-2 is a part of the Toll-like 4 signaling complex with an indispensable role in activation of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) signaling pathway and thus a suitable target for the therapeutic inhibition of TLR4 signaling. Elucidation of MD-2 structure provides a foundation for rational design of inhibitors that bind to MD-2 and inhibit LPS signaling. Since the hydrophobic binding pocket of MD-2 provides little specificity for inhibitors, we have investigated targeting the solvent-accessible cysteine residue within the hydrophobic binding pocket of MD-2. Compounds with affinity for the hydrophobic pocket that contain a thiol-reactive group, which mediates covalent bond formation with the free cysteine residue of MD-2, were tested. Fluorescent compounds 2-(4'-(iodoacetamido)anilino)naphthalene-6-sulfonic acid and N-pyrene maleimide formed a covalent bond with MD-2 through Cys(133) and inhibited LPS signaling. Cell activation was also inhibited by thiol-reactive compounds JTT-705 originally targeted against cholesterol ester transfer protein and antirheumatic compound auranofin. Oral intake of JTT-705 significantly inhibited endotoxin-triggered tumor necrosis factor alpha production in mice. The thiol group of MD-2 also represents the target of environmental or endogenous thiol-reactive compounds that are produced in inflammation.
Figures
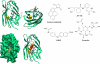



Similar articles
-
Identification of synthetic peptides that inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding to myeloid differentiation protein-2 (MD-2).J Immunother. 2013 Apr;36(3):197-207. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e31828eed62. J Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23502767
-
Lysines 128 and 132 enable lipopolysaccharide binding to MD-2, leading to Toll-like receptor-4 aggregation and signal transduction.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 28;278(48):48313-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306802200. Epub 2003 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12960171
-
Essential roles of hydrophobic residues in both MD-2 and toll-like receptor 4 in activation by endotoxin.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 29;284(22):15052-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M901429200. Epub 2009 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19321453 Free PMC article.
-
Structural model of MD-2 and functional role of its basic amino acid clusters involved in cellular lipopolysaccharide recognition.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 2;279(27):28475-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400993200. Epub 2004 Apr 24. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15111623
-
Pharmacological inhibition of endotoxin responses is achieved by targeting the TLR4 coreceptor, MD-2.J Immunol. 2005 Nov 15;175(10):6465-72. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.10.6465. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16272300
Cited by
-
The biological activity of auranofin: implications for novel treatment of diseases.Inflammopharmacology. 2012 Dec;20(6):297-306. doi: 10.1007/s10787-012-0149-1. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Inflammopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22965242 Review.
-
Biochemical characterization of cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors.J Lipid Res. 2010 Sep;51(9):2739-52. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M007468. Epub 2010 May 10. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20458119 Free PMC article.
-
Gram Negative Bacterial Inflammation Ameliorated by the Plasma Protein Beta 2-Glycoprotein I.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 27;6:33656. doi: 10.1038/srep33656. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27670000 Free PMC article.
-
Kdo2 -lipid A: structural diversity and impact on immunopharmacology.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2015 May;90(2):408-27. doi: 10.1111/brv.12114. Epub 2014 May 16. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2015. PMID: 24838025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the 3CL Protease and SARS-CoV-2 Replication by Dalcetrapib.ACS Omega. 2021 Jun 17;6(25):16584-16591. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01797. eCollection 2021 Jun 29. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34235330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Viriyakosol S., Tobias P. S., Kitchens R. L., Kirkland T. N. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 38044–38051 - PubMed
-
- Nagai Y., Akashi S., Nagafuku M., Ogata M., Iwakura Y., Akira S., Kitamura T., Kosugi A., Kimoto M., Miyake K. (2002) Nat. Immunol. 3, 667–672 - PubMed
-
- Saitoh S., Akashi S., Yamada T., Tanimura N., Kobayashi M., Konno K., Matsumoto F., Fukase K., Kusumoto S., Nagai Y., Kusumoto Y., Kosugi A., Miyake K. (2004) Int. Immunol 16, 961–969 - PubMed
-
- Visintin A., Halmen K. A., Latz E., Monks B. G., Golenbock D. T. (2005) J. Immunol. 175, 6465–6472 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

