Invasion of endothelial cells by tissue-invasive M3 type group A streptococci requires Src kinase and activation of Rac1 by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent mechanism
- PMID: 19473989
- PMCID: PMC2740457
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.016501
Invasion of endothelial cells by tissue-invasive M3 type group A streptococci requires Src kinase and activation of Rac1 by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent mechanism
Abstract
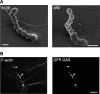
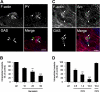
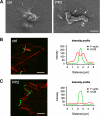
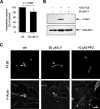
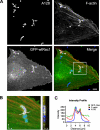
Streptococcus pyogenes can cause invasive diseases in humans, such as sepsis or necrotizing fasciitis. Among the various M serotypes of group A streptococci (GAS), M3 GAS lacks the major epithelial invasins SfbI/PrtF1 and M1 protein but has a high potential to cause invasive disease. We examined the uptake of M3 GAS into human endothelial cells and identified host signaling factors required to initiate streptococcal uptake. Bacterial uptake is accompanied by local F-actin accumulation and formation of membrane protrusions at the entry site. We found that Src kinases and Rac1 but not phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3Ks) are essential to mediate S. pyogenes internalization. Pharmacological inhibition of Src activity reduced bacterial uptake and abolished the formation of membrane protrusions and actin accumulation in the vicinity of adherent streptococci. We found that Src kinases are activated in a time-dependent manner in response to M3 GAS. We also demonstrated that PI3K is dispensable for internalization of M3 streptococci and the formation of F-actin accumulations at the entry site. Furthermore, Rac1 was activated in infected cells and accumulated with F-actin in a PI3K-independent manner at bacterial entry sites. Genetic interference with Rac1 function inhibited streptococcal internalization, demonstrating an essential role of Rac1 for the uptake process of streptococci into endothelial cells. In addition, we demonstrated for the first time accumulation of the actin nucleation complex Arp2/3 at the entry port of invading M3 streptococci.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bacillus anthracis spore entry into epithelial cells is an actin-dependent process requiring c-Src and PI3K.PLoS One. 2010 Jul 20;5(7):e11665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011665. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20652027 Free PMC article.
-
Invasion of endothelial cells by Neisseria meningitidis requires cortactin recruitment by a phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Rac1 signalling pathway triggered by the lipo-oligosaccharide.J Cell Sci. 2005 Aug 15;118(Pt 16):3805-16. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02514. Epub 2005 Aug 2. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16076899
-
Cdc42 and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway are essential for PspC-mediated internalization of pneumococci by respiratory epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 17;284(29):19427-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.003442. Epub 2009 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19473971 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesion and invasion of Streptococcus pyogenes into host cells and clinical relevance of intracellular streptococci.2022 Sep 4 [updated 2022 Oct 4]. In: Ferretti JJ, Stevens DL, Fischetti VA, editors. Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations [Internet]. 2nd edition. Oklahoma City (OK): University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center; 2022 Oct 8. Chapter 17. 2022 Sep 4 [updated 2022 Oct 4]. In: Ferretti JJ, Stevens DL, Fischetti VA, editors. Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations [Internet]. 2nd edition. Oklahoma City (OK): University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center; 2022 Oct 8. Chapter 17. PMID: 36479770 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Adhesion and invasion of Streptococcus pyogenes into host cells and clinical relevance of intracellular streptococci.2016 Feb 10. In: Ferretti JJ, Stevens DL, Fischetti VA, editors. Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations [Internet]. Oklahoma City (OK): University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center; 2016–. 2016 Feb 10. In: Ferretti JJ, Stevens DL, Fischetti VA, editors. Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations [Internet]. Oklahoma City (OK): University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center; 2016–. PMID: 26866223 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular Invasion by Streptococcus pyogenes: Invasins, Host Receptors, and Relevance to Human Disease.Microbiol Spectr. 2019 Jul;7(4):10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0049-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0049-2018. Microbiol Spectr. 2019. PMID: 31267891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor-mediated invasion of Streptococcus pneumoniae into host cells requires a coordinate signaling of SRC family of protein-tyrosine kinases, ERK, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 12;285(46):35615-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.172999. Epub 2010 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20829350 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between group A Streptococcus and host innate immune responses.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Mar 27;88(1):e0005222. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00052-22. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38451081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The M1 protein of Streptococcus pyogenes triggers an innate uptake mechanism into polarized human endothelial cells.J Innate Immun. 2014;6(5):585-96. doi: 10.1159/000358085. Epub 2014 Jan 31. J Innate Immun. 2014. PMID: 24504091 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the genetic toolbox for the obligate human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 7;12:1395659. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1395659. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38911550 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

