Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein plays a major role in induction of the fish innate immune response against RNA and DNA viruses
- PMID: 19474100
- PMCID: PMC2715792
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00404-09
Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein plays a major role in induction of the fish innate immune response against RNA and DNA viruses
Abstract
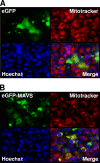
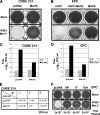
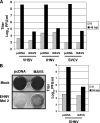
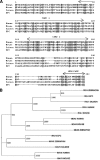
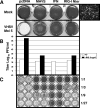
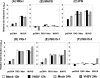
Viral infection triggers host innate immune responses through cellular sensor molecules which activate multiple signaling cascades that induce the production of interferons (IFN) and other cytokines. The recent identification of mammalian cytoplasmic viral RNA sensors, such as retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs) and their mitochondrial adaptor, the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS), also called IPS-1, VISA, and Cardif, highlights the significance of these molecules in the induction of IFN. Teleost fish also possess a strong IFN system, but nothing is known concerning the RLRs and their downstream adaptor. In this study, we cloned MAVS cDNAs from several fish species (including salmon and zebrafish) and showed that they were orthologs of mammalian MAVS. We demonstrated that overexpression of these mitochondrial proteins in fish cells led to a constitutive induction of IFN and IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs). MAVS-overexpressing cells were almost fully protected against RNA virus infection, with a strong inhibition of both DNA and RNA virus replication (1,000- and 10,000-fold decreases, respectively). Analyses of MAVS deletion mutants showed that both the N-terminal CARD-like and C-terminal transmembrane domains, but not the central proline-rich region, were indispensable for MAVS signaling function. In addition, we cloned the cDNAs encoding a RIG-I-like molecule from salmonid and cyprinid cell lines. Like the case with MAVS, overexpression of RIG-I CARDs in fish cells led to a strong induction of both IFN and ISGs, conferring on fish cells full protection against RNA virus infection. This report provides the first demonstration that teleost fish possess a functional RLR pathway in which MAVS may play a central role in the induction of the innate immune response.
Figures

References
-
- Beutler, B., C. Eidenschenk, K. Crozat, J. L. Imler, O. Takeuchi, J. A. Hoffmann, and S. Akira. 2007. Genetic analysis of resistance to viral infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7753-766. - PubMed
-
- Boudinot, P., S. Riffault, S. Salhi, C. Carrat, C. Sedlik, N. Mahmoudi, B. Charley, and A. Benmansour. 2000. Vesicular stomatitis virus and pseudorabies virus induce a vig1/cig5 homologue in mouse dendritic cells via different pathways. J. Gen. Virol. 812675-2682. - PubMed
-
- Boudinot, P., S. Salhi, M. Blanco, and A. Benmansour. 2001. Viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus induces vig-2, a new interferon-responsive gene in rainbow trout. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 11383-397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

