Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for infectious and inflammatory diseases and cancer
- PMID: 19474110
- PMCID: PMC2846156
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.109.001073
Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for infectious and inflammatory diseases and cancer
Abstract
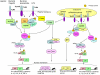
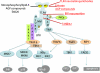
Since first being described in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, Toll-like receptors (TLRs) have proven to be of great interest to immunologists and investigators interested in the molecular basis to inflammation. They recognize pathogen-derived factors and also products of inflamed tissue, and trigger signaling pathways that lead to activation of transcription factors such as nuclear factor-kappaB and the interferon regulatory factors. These in turn lead to induction of immune and inflammatory genes, including such important cytokines as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and type I interferon. Much evidence points to a role for TLRs in immune and inflammatory diseases and increasingly in cancer. Examples include clear roles for TLR4 in sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, ischemia/reperfusion injury, and allergy. TLR2 has been implicated in similar pathologic conditions and also in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and tumor metastasis. TLR7 has also been shown to be important in SLE. TLR5 has been shown to be radioprotective. Recent advances in our understanding of signaling pathways activated by TLRs, structural insights into TLRs bound to their ligands and antagonists, and approaches to inhibit TLRs (including antibodies, peptides, and small molecules) are providing possiblemeans by which to interfere with TLRs clinically. Here we review these recent advances and speculate about whether manipulating TLRs is likely to be successful in fighting off different diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor signaling in colorectal cancer: carcinogenesis to cancer therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 21;20(47):17699-708. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17699. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25548469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Toll-like receptors: emerging therapeutics?Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Apr;9(4):293-307. doi: 10.1038/nrd3203. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 20380038 Review.
-
Toll-like receptors: cost or benefit for cancer?Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(9):1081-90. doi: 10.2174/138161210790963779. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20030618 Review.
-
Antagonist-mediated down-regulation of Toll-like receptors increases the prevalence of human papillomavirus infection in systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Apr 18;14(2):R80. doi: 10.1186/ar3803. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22513098 Free PMC article.
-
Primer: Toll-like receptor signaling pathways--what do rheumatologists need to know?Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008 Jun;4(6):319-27. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum0802. Epub 2008 Apr 29. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18446139 Review.
Cited by
-
Controlling complexity: the clinical relevance of mouse complex genetics.Eur J Hum Genet. 2013 Nov;21(11):1191-6. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.79. Epub 2013 May 1. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23632795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteasome protease mediated regulation of cytokine induction and inflammation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Nov;1823(11):2087-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.06.016. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22728331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of small-molecule inhibitors of the TLR1/TLR2 complex.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012 Dec 3;51(49):12246-9. doi: 10.1002/anie.201204910. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012. PMID: 22969053 Free PMC article.
-
Association between small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and toll-like receptor 4 in patients with pancreatic carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb;30(2):177-183. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2018.17512. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30457560 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 activation in Barrett's esophagus results in a strong increase in COX-2 expression.J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul;49(7):1121-34. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0862-6. Epub 2013 Aug 17. J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 23955118
References
-
- Agrawal S and Kandimalla ER (2007) Synthetic agonists of Toll-like receptors 7, 8 and 9. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1461-1467. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad-Nejad P, Mrabet-Dahbi S, Breuer K, Klotz M, Werfel T, Herz U, Heeg K, Neumaier M, and Renz H (2004) The toll-like receptor 2 R753Q polymorphism defines a subgroup of patients with atopic dermatitis having severe phenotype. J Allergy Clin Immunol 113:565-567. - PubMed
-
- Akashi S, Nagai Y, Ogata H, Oikawa M, Fukase K, Kusumoto S, Kawasaki K, Nishijima M, Hayashi S, Kimoto M, et al. (2001) Human MD-2 confers on mouse Toll-like receptor 4 species-specific lipopolysaccharide recognition. Int Immunol 13:1595-1599. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, and Flavell RA (2001) Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413:732-738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

